Towards an AI-based Transportation Monitoring System using Campus Video Footage: Early Experiments in Vehicle Detection and Tracking
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/aaij.3.1.19Keywords:
AI-based monitoring, vehicle tracking, carbon emission estimation, campus environmentAbstract
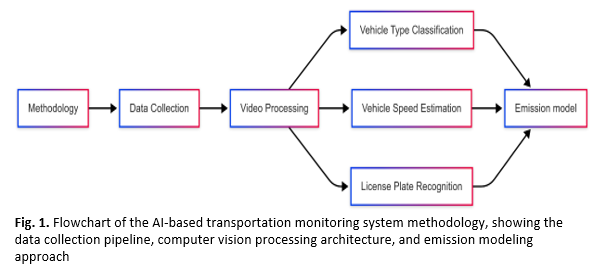
This paper presents early experimental results towards developing an AI-based transportation monitoring system using campus video footage at Universiti Malaya. Manual traffic monitoring is inefficient, and the lack of automated systems makes real-time tracking and carbon emission estimation particularly challenging in campus environments. The primary objective is to develop a system capable of accurately detecting and tracking vehicles, identifying vehicle types, recognizing license plates, and estimating vehicle speeds. This data, particularly vehicle speed, is crucial for subsequent estimation of carbon emissions, a key parameter for comprehensive campus transportation monitoring. Our methodology involved capturing video data at various strategic locations within the Universiti Malaya campus using a single, fixed handheld camera. We employed a robust AI pipeline leveraging YOLOv8 for vehicle detection and tracking, a custom-trained YOLO model for license plate detection, and EasyOCR for optical character recognition of license plates. Preliminary experiments demonstrate the system's ability to track individual vehicles, classify them by type, and extract license plate information, along with real-time speed estimation. Challenges related to camera resolution, placement trade-offs for optimal detection, and deployment logistics were identified. This work lays the foundation for a more comprehensive, real-time transportation monitoring system, with future efforts focusing on improving accuracy, optimizing for edge deployment, and integrating multi-camera data for enhanced environmental impact assessment.