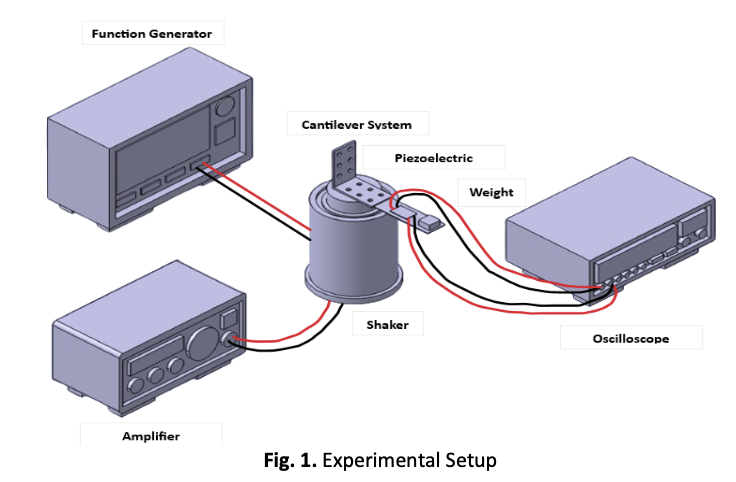
Optimization of SnO₂ Concentration in PVDF-Based Piezoelectric Nanocomposites for Enhanced Energy Harvesting at Low Frequencies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arca.39.1.181195Keywords:
Piezoelectric, Cantilever Beam, vibration energy harvesting, Polyvinyledene Flouride (PVDF), tin oxideAbstract
This study investigates the influence of varying SnO₂ concentrations in PVDF-based piezoelectric nanocomposites on electrical output under different frequency conditions. Three different weight percentages (3 wt%, 5 wt%, and 7 wt%) were tested to determine the optimal concentration for energy harvesting applications. The results revealed that a 5 wt% SnO₂ concentration produced the highest electrical output, achieving a peak voltage of 0.6 V and maximum power at approximately 6 Hz, which aligns with the system’s natural resonance frequency. Higher SnO₂ concentrations (7 wt%) resulted in reduced performance due to increased stiffness, while the lower concentration (3 wt%) showed consistent output but lower peak values, demonstrating its suitability for stable, low-frequency applications. These findings emphasize the importance of material composition and frequency optimization for enhancing energy conversion efficiency in piezoelectric systems. The study contributes valuable insights into the design of piezoelectric energy harvesting devices, particularly for applications in low-frequency environments.