Enhancing Environmental Monitoring in Gold Mining: A Systematic Review of IoT Sensors and Technologies for Effective Hazardous Waste Detection
Keywords:
Internet of Things, monitoring, gold mines, sensor detections, hazardous wasteAbstract
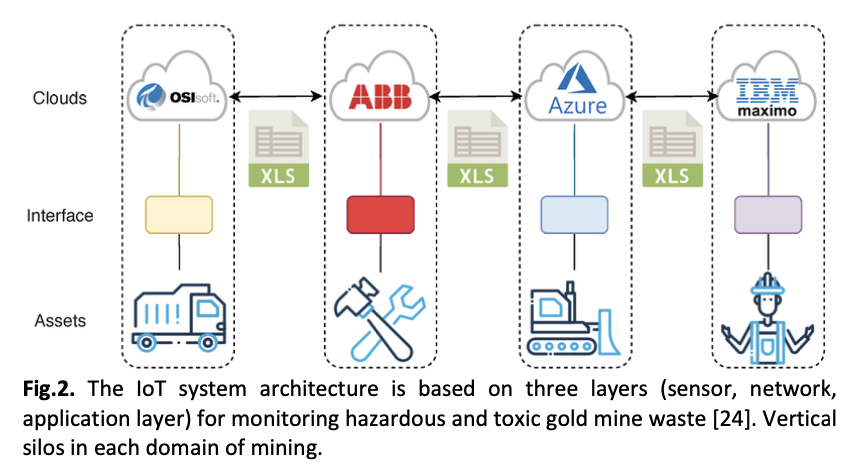
Gold mining contributes significantly to the economy but generates hazardous waste and toxic waste such as mercury and cyanide, posing serious environmental threats. Conventioal monitoring methods are outdated and lack real-time detection. This study aims to review recent applications of Internet of Things (IoT) technology for hazardous waste and toxic waste monitoring in gold mining. Using a systematic review of 35 publications (2015–2025), the study examines system architecture, sensor types, communication protocols, and implementation challenges. Results show that effective systems integrate multi-parameter sensors (pH, heavy metals, hazardous gases), low-power communication (LoRa, ZigBee), and real-time monitoring platforms. Key challenges include harsh environments, network limitations, and sensor maintenance, with solutions involving robust design and advanced analytics. The incorporation of artificial intelligence, including Edge AI and machine learning, enhances predictive and anomaly detection capabilities. IoT-based monitoring improves accuracy, efficiency, and sustainability, supporting more proactive environmental risk management in gold mining.