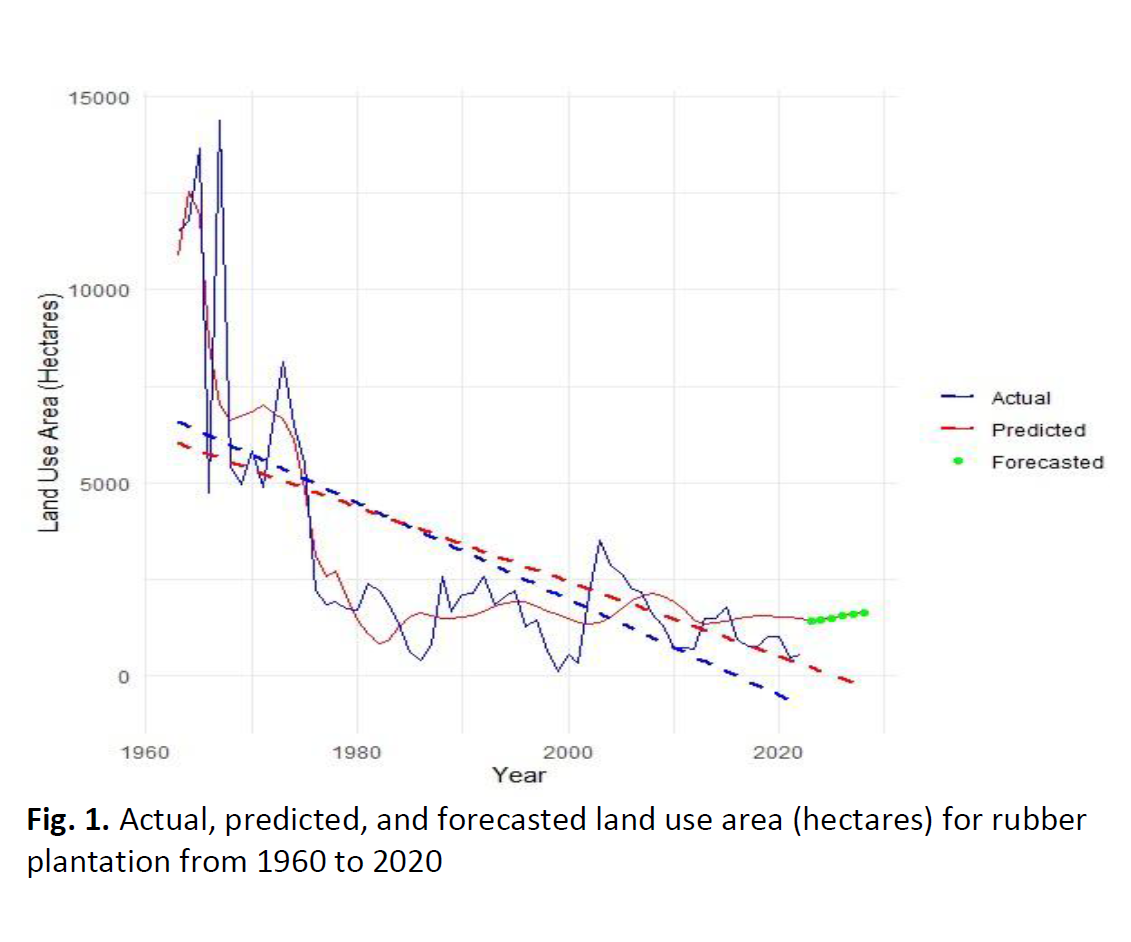
Forecasting Land Use Trends using Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Rubber Plantations in Johor
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sea.4.1.3242aKeywords:
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM), land use forecasting, rubber plantations, Johor, time series analysisAbstract
In this paper, we use LSTM to predict the future land-use trend based on trends from within rubber plantations in Johor state of Malaysia. These predictions are particularly important for improved agricultural planning and policy, which rely on accurate estimates of how land use may change over long time periods. The purpose of this study is to build a powerful prediction model, i.e., an LSTM network. The paper details the training procedure, introduces model architecture and several data pre-processing methods. In other terms, time series analysis is used to see the patterns or trends in historical data. The model is evaluated based on its performance measures (e.g., accuracy and consistency). The findings showed that the LSTM networks are able to perform reliable prediction by land usage in Johor, granting much-required knowledge essential for agriculture planning and polices making. The main findings of this paper are that LSTM networks can be used to forecast land use changes and help in long-term strategic planning for rubber plantations in Johor.