Exploratory Research on AI Empowerment in the Management of Higher Education Institutions in Zhejiang from an ESG Perspective
Keywords:
Sustainable development, ESG, higher education, AIAbstract
Against the global sustainable development backdrop, Chinese universities have shortcomings in advancing sustainable development, including ambiguous Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) awareness in the academic community, lack of quantitative campus sustainable development assessment mechanisms, and no collaboration mechanism among university administrators, teachers, and students. With Artificial Intelligence (AI)’s rapid development, there is a new way to solve this predicament, and Zhejiang has the foundation to integrate sustainable development with AI. This paper adopts descriptive analysis to explore the differences in students' ESG awareness levels. Then, using K-means clustering analysis, it conducts unsupervised segmentation of student groups based on core variables such as ESG awareness and AI acceptance, identifies typical behavioral patterns, and portrays group profiles. Meanwhile, it identifies key weak links based on the current status of ESG management, constructs a model of influencing factors on campus ESG management effectiveness by combining multiple linear regression, and reveals the mechanism of action of these influencing factors. Finally, it uses the forward LR method to construct a binary Logistic regression model, revealing how demographic characteristics and cognitive levels affect individuals' willingness to support ESG practices.
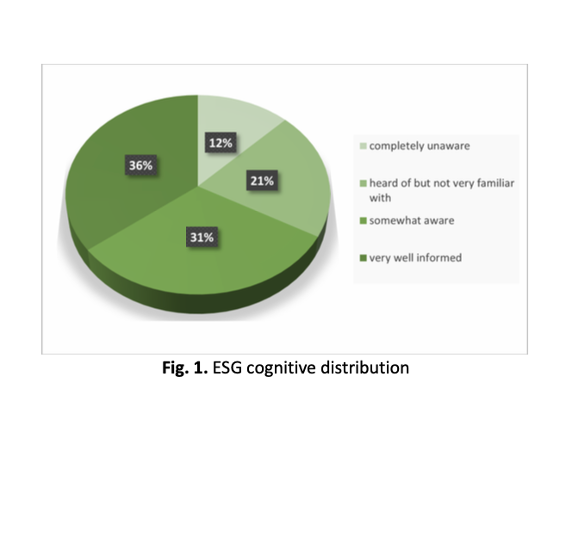
The research yields the following outcomes, (1) University ESG promotion has initial achievements but faces superficial student cognition and general wait-and-see attitudes toward AI-empowered ESG; (2) Students’ environmental participation and ESG environmental goals significantly impact university management effectiveness; (3) AI empowerment is largely influenced by students’ environmental values. This study has the following significance, (1) It contributes to the achievement of SDG.11 (Sustainable Development Goal 11) of the global sustainable development goals; (2) It constructs an "ESG + AI" management framework, enabling universities to become "micro-units" in global sustainable development practices; (3) Taking advantage of the popularity of AI technology, it leverages AI's capabilities in intelligent monitoring and in-depth analysis of massive and complex ESG data to reshape a data-driven ESG practice model.