Analysis of Lossless Compression in Huffman Coding and Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/arca.39.1.110Keywords:
Data compression, lossless compression, QR code, Huffman Coding, Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW)Abstract
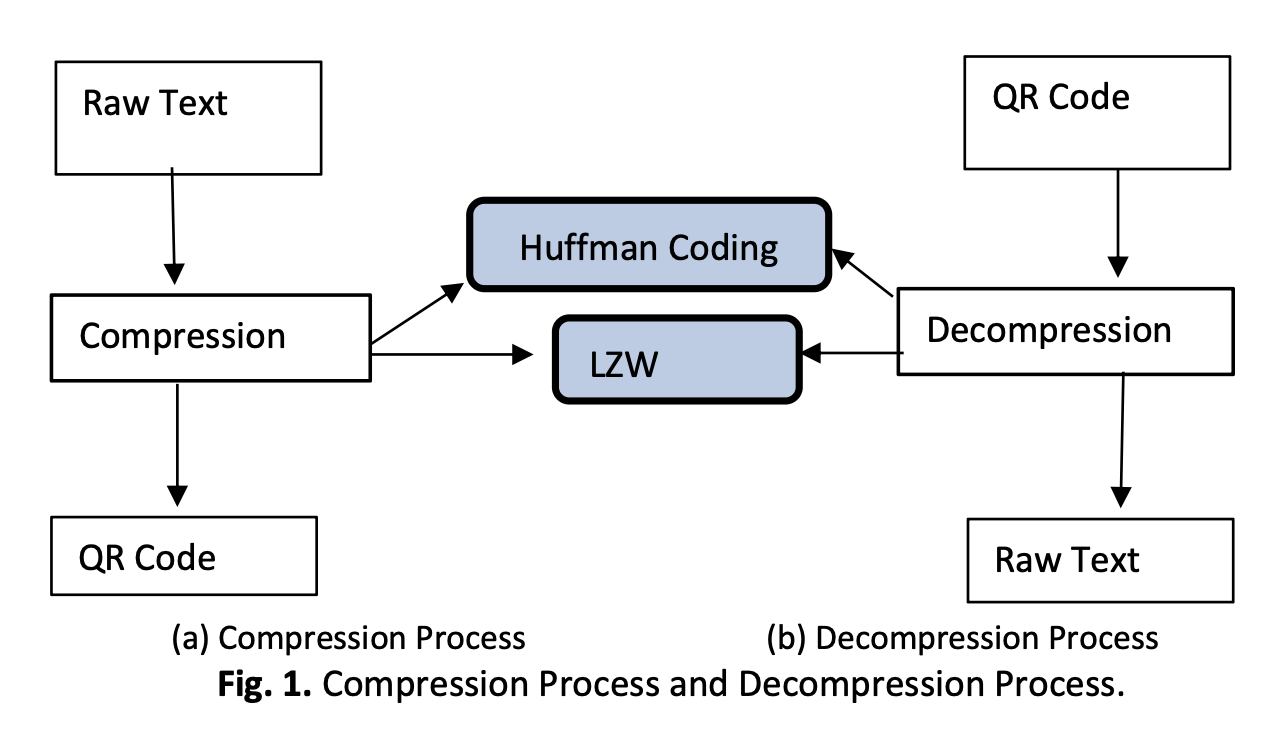
Two-dimensional barcodes called Quick Response codes (QR codes) are commonly used to store data, such as URLs, contact details, and product details. As a means of information sharing, they are growing in popularity due to their ability to store large amounts of data in a small footprint. However, the increasing demand for data storage necessitates larger QR code sizes, potentially impacting readability and scanning efficiency. This study looks into how to use lossless compression techniques like Huffman Coding and Lempel-Ziv-Welch (LZW) to make QR codes store more information without losing any of their accuracy. According to the tests, LZW had an average compression ratio of 35%, and Huffman coding had 40%. This demonstrated that both approaches could considerably compress QR code sizes. Furthermore, both methods ensured reliability by maintaining 100% data integrity after decoding. The results show that adding lossless compression to QR codes makes them work better, which means they can be used to store more data in smaller spaces. This research provides a foundation for further advancements in QR code optimisation, particularly in multi-layered and multicoloured QR code systems.