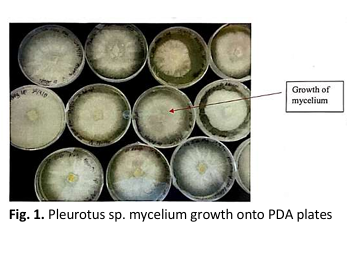
Evaluation of Antioxidant and Phytochemical Properties of Pleurotus sp. Mushroom Mycelium
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/fsat.5.1.2842Keywords:
Pleurotus sp., antioxidant, phytochemical, ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis(3- ethylbenzothiazoline-6- sulfonic acid), reactive oxigen speciesAbstract
Pleurotus sp. mycelium is well-known for its therapeutic properties, since it contains a variety of bioactive compounds with antioxidant and phytochemical features. Pleurotus sp. mushroom research involves growing the mycelium in optimal conditions with sufficient nutrients to yield a large amount of biomass. The mushroom mycelium was grown using the submerged fermentation method, which provided enough nutrients to produce a large amount of mycelium. Hot water extraction yielded more extract and bioactive component than cold water extraction, with a dextrose equivalent of 0.913. To determine the effect of antioxidant properties on inhibiting the formation of free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS), phytochemical screening was used to identify bioactive components in mushroom extracts. Antioxidant effectiveness using the ABTS assay was critical when compared to ascorbic acid as the antioxidant standard. Pleurotus sp. mushroom mycelium inhibits free radicals and indicates the antioxidant and phytochemical activity.