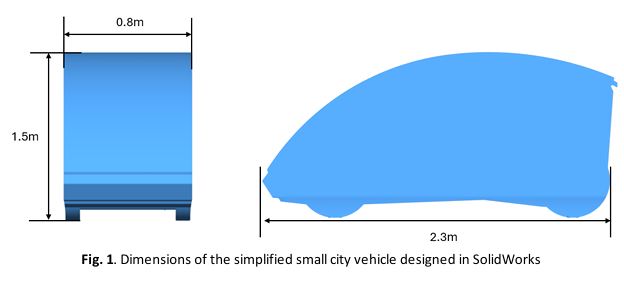
Numerical Analysis on Impact of Crosswinds on the Aerodynamic Performance of Small City Vehicles
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/javs.16.1.1022Keywords:
Aerodynamic, computational fluid dynamics, crosswinds, Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS), small city vehiclesAbstract
Small city vehicles are particularly vulnerable to crosswinds due to their lightweight design and higher center of gravity, which reduce stability. Additionally, their aerodynamic shapes can generate lift, making them more susceptible to being pushed off course in windy conditions. This study investigates the aerodynamics of small city vehicles using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) with the Reynolds-Averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) approach in ANSYS Fluent. The focus is on analyzing the aerodynamic performance of a small city vehicle at a constant speed while subjected to four different crosswind angles: 15°, 30°, 45°, and 60°. A mesh refinement study is conducted to validate the simulations, comparing results from three different mesh configurations to ensure accuracy and reliability. The results indicate that the side force coefficient increases from 1.5 to 5 as the crosswind angle reaches 60°. Additionally, the drag coefficient is observed to be highest at the 30° crosswind angle and decreases to its minimum at the highest crosswind angle. Flow structures show significant complexity at higher crosswind angles. These findings highlight the intricate interactions between the vehicle and crosswinds, providing valuable insights for optimizing the aerodynamic design of small city vehicles to enhance their stability and performance in urban environments.