Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Smart Construction: A PRISMA-Based Systematic Review
Memanfaatkan Kecerdasan Buatan untuk Pembinaan Pintar Mampan: Satu Kajian Sistematik Berasaskan PRISMA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/progee.31.2.101119Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence, Construction, Digital Transformation, Smart Construction, Sustainable, Kecerdasan Buatan, Pembinaan, Transformasi Digital, Pembinaan Pintar, MampanAbstract
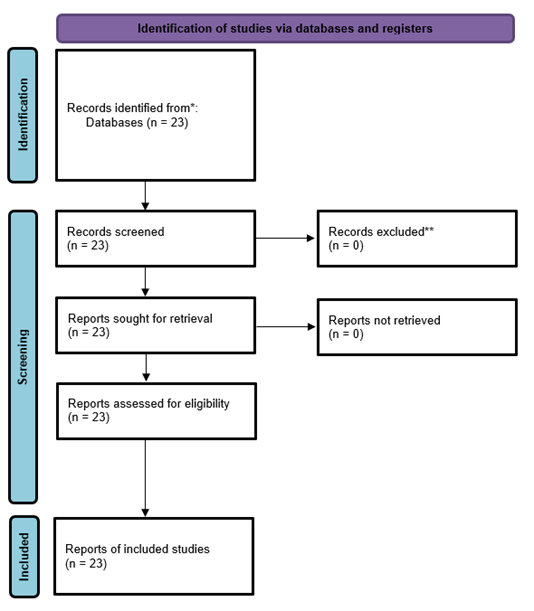
The construction industry is undergoing a significant technological transformation, with Artificial Intelligence (AI) playing a pivotal role in improving efficiency, sustainability, and decision-making. As complex projects evolve, traditional manual methods often lead to inefficiencies, delays, and increased safety risks. AI has emerged as a vital tool for optimizing construction processes, though there remains an incomplete understanding of its applications across various project stages. This study systematically identifies key AI applications that enhance smart construction throughout planning, design, execution, operation, and demolition phases. A Systematic Literature Review (SLR) was employed following the PRISMA framework, leading to the collection of 23 relevant articles from the Web of Science database. Descriptive and bibliometric analyses were conducted using VOSviewer to assess publication trends, research methodologies, geographical distribution, and the co-occurrence of AI-related keywords. Findings indicate that AI significantly aids in predictive analytics for risk assessment, generative design, construction monitoring, safety management, supply chain optimization, energy efficiency, and smart maintenance through digital twins. Furthermore, AI advances real-time site monitoring, waste sorting, and sustainability-driven deconstruction planning, which supports the implementation of the circular economy in construction. This study provides a structured overview of AI’s contribution to smart construction, offering insights to academics, policymakers, and industry professionals on driving the integration of AI in the built environment. The goal is to foster safer, more efficient, and sustainable construction practices in the future.
Industri pembinaan sedang mengalami transformasi teknologi, dengan Kecerdasan Buatan (AI) memainkan peranan penting dalam meningkatkan kecekapan, kemampanan, dan pembuatan keputusan. Seiring dengan peningkatan kompleksiti projek pembinaan, kaedah manual tradisional dan berasaskan pengalaman sering menyebabkan ketidakcekapan, kelewatan, lebihan kos, serta risiko keselamatan. AI telah muncul sebagai alat yang berkuasa untuk mengoptimumkan proses pembinaan, namun masih terdapat kekurangan pemahaman yang menyeluruh mengenai aplikasinya dalam pelbagai peringkat projek. Kajian ini bertujuan untuk mengenal pasti secara sistematik aplikasi utama AI dalam mempromosikan pembinaan pintar sepanjang fasa perancangan, reka bentuk, pelaksanaan, operasi, dan perobohan. Kajian Sistematik (SLR) telah dijalankan menggunakan rangka kerja PRISMA, dengan 23 artikel berkaitan diperoleh daripada pangkalan data Web of Science. Analisis deskriptif dan bibliometrik telah dilakukan menggunakan VOSviewer bagi meneliti trend penerbitan, metodologi penyelidikan, taburan geografi, serta kejadian bersama kata kunci berkaitan AI. Penemuan kajian menunjukkan bahawa AI memberikan sumbangan yang ketara dalam analitik ramalan untuk penilaian risiko, reka bentuk generatif, pemantauan pembinaan automatik, pengurusan keselamatan, pengoptimuman rantaian bekalan, kecekapan tenaga, serta penyelenggaraan pintar melalui kembar digital. Selain itu, AI juga meningkatkan pemantauan tapak secara masa nyata, penyisihan sisa, dan perancangan pembongkaran berorientasikan kemampanan, sekali gus menyokong ekonomi kitaran dalam industri pembinaan. Kajian ini menyumbang dengan menyediakan gambaran terstruktur mengenai peranan AI dalam pembinaan pintar, serta menawarkan pandangan bernilai kepada ahli akademik, pembuat dasar, dan profesional industri dalam mendorong integrasi AI di persekitaran binaan. Akhirnya, ini membawa kepada amalan pembinaan yang lebih selamat, cekap, dan mampan.
References
[1] S.O. Abioye, L.O. Oyedele, L. Akanbi, A. Ajayi, J.M. Davila Delgado, M. Bilal, O.O. Akinade, and A. Ahmed, Artificial Intelligence in the Construction Industry: A Review of Present Status, Opportunities and Future Challenges, Journal of Building Engineering 44 (2021) 103299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103299.
[2] M. Regona, T. Yigitcanlar, B. Xia, and R.Y.M. Li, Opportunities and Adoption Challenges of AI in the Construction Industry: A PRISMA Review, Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 8 (2022) 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc8010045.
[3] M. Baghalzadeh Shishehgarkhaneh, A. Keivani, R.C. Moehler, N. Jelodari, and S. Roshdi Laleh, Internet of Things (IoT), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and Digital Twin (DT) in Construction Industry: A Review, Bibliometric, and Network Analysis, Buildings 12 (2022) 1503. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12101503.
[4] M.-A. Vigneault, C. Boton, H.-Y. Chong, and B. Cooper-Cooke, An Innovative Framework of 5D BIM Solutions for Construction Cost Management: A Systematic Review, Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 27 (2020) 1013-1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-019-09341-z.
[5] J.M. Davila Delgado, and L. Oyedele, Digital Twins for the Built Environment: Learning from Conceptual and Process Models in Manufacturing, Advanced Engineering Informatics 49 (2021) 101332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2021.101332.
[6] L.A. Akanbi, A.O. Oyedele, L.O. Oyedele, and R.O. Salami, Deep Learning Model for Demolition Waste Prediction in a Circular Economy, Journal of Cleaner Production 274 (2020) 122843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.1228430.
[7] C. Mocerino, Digital Revolution in Efficient Self-Organization of Buildings: Towards Intelligent Robotics, 2018 Energy and Sustainability for Small Developing Economies (ES2DE), 2018, pp. 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ES2DE.2018.8494237.
[8] S. Agostinelli, F. Cumo, G. Guidi, and C. Tomazzoli, Cyber-Physical Systems Improving Building Energy Management: Digital Twin and Artificial Intelligence, Energies 14 (2021) 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14082338.
[9] M. Afzal, R.Y.M. Li, M. Shoaib, M.F. Ayyub, L.C. Tagliabue, M. Bilal, H. Ghafoor, and O. Manta, Delving into the Digital Twin Developments and Applications in the Construction Industry: A PRISMA Approach, Sustainability 15 (2023) 16436. https://doi.org/10.3390/su152316436.
[10] A.J. Sánchez-Garrido, I.J. Navarro, J. García, V. Yepes, A Systematic Literature Review on Modern Methods of Construction in Building: An Integrated Approach using Machine Learning, Journal of Building Engineering 73 (2023) 106725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.106725.
[11] L. Zhang, Y. Li, Y. Pan, and L. Ding, Advanced Informatic Technologies for Intelligent Construction: A Review, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 137 (2024) 109104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2024.109104.
[12] Z. Liu, Y. He, P. Demian, and M. Osmani, Immersive Technology and Building Information Modeling (BIM) for Sustainable Smart Cities, Buildings 14 (2024) 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings14061765.
[13] B.C. Weber-Lewerenz, M. Traverso, Best Practices in Construction 4.0 – Catalysts of digital innovations (Part I), Journal of Architectural Environment & Structural Engineering Research (2023).
[14] A.F. Kineber, N. Elshaboury, A.E. Oke, J. Aliu, Z. Abunada, and M. Alhusban, Revolutionizing Construction: A Cutting-Edge Decision-Making Model for Artificial Intelligence Implementation in Sustainable Building Projects, Heliyon 10 (2024) e37078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37078.
[15] S.K. Yevu, E.K. Owusu, A.P.C. Chan, S.M.E. Sepasgozar, and V.R. Kamat, Digital Twin-Enabled Prefabrication Supply Chain for Smart Construction and Carbon Emissions Evaluation in Building Projects, Journal of Building Engineering 78 (2023) 107598. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2023.107598.
[16] O. Sánchez, K. Castañeda, S. Vidal-Méndez, D. Carrasco-Beltrán, and N.E. Lozano-Ramírez, Exploring the Influence of Linear Infrastructure Projects 4.0 Technologies to Promote Sustainable Development in Smart Cities, Results in Engineering 23 (2024) 102824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102824.
[17] M. Regona, T. Yigitcanlar, C.K.H. Hon, and M. Teo, Mapping Two Decades of AI in Construction Research: A Scientometric Analysis from the Sustainability and Construction Phases Lenses, Buildings 13 (2023) 2346. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings13092346.
[18] J. de Almeida Barbosa Franco, A.M. Domingues, N. de Almeida Africano, R.M. Deus, and R.A.G. Battistelle, Sustainability in the Civil Construction Sector Supported by Industry 4.0 Technologies: Challenges and Opportunities, Infrastructures 7 (2022) 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7030043.
[19] H. Shafei, R.A. Rahman, and Y.S. Lee, Construction 4.0 Technology Evaluation using Fuzzy TOPSIS: Comparison between Sustainability and Resiliency, Well-being, Productivity, Safety, and Integrity, Environmental Science and Pollution Research 31 (2024) 14858-14893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-31862-9.
[20] H. Aladağ, İ. Güven, and O. Balli, Contribution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) to Construction Project Management Processes: State of the Art with Scoping Review Method, Sigma Journal of Engineering and Natural Sciences 42 (2024) 1654-1669.
[21] J. Zhang, X. Zhu, A.M. Khan, M. Houda, S. Kashif Ur Rehman, M. Jameel, M.F. Javed, and R. Alrowais, BIM-based Architectural Analysis and Optimization for Construction 4.0 Concept (A Comparison), Ain Shams Engineering Journal 14 (2023) 102110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2022.102110.
[22] Y. Jiang, S. Su, S. Zhao, R.Y. Zhong, W. Qiu, M.J. Skibniewski, I. Brilakis, and G.Q. Huang, Digital Twin-Enabled Synchronized Construction Management: A Roadmap from Construction 4.0 towards Future Prospect, Developments in the Built Environment 19 (2024) 100512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dibe.2024.100512.
[23] G. Qiang, S. Tang, J. Hao, and L.D. Sarno, A BIM and AIoT Integration Framework for Improving Energy Efficiency in Green Buildings, Construction Research Congress 2024, 2024, pp. 577-585. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784485262.059.
[24] R. Sacks, M. Girolami, and I. Brilakis, Building Information Modelling, Artificial Intelligence and Construction Tech, Developments in the Built Environment 4 (2020) 100011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dibe.2020.100011.
[25] Y. Xu, Y. Zhou, P. Sekula, and L. Ding, Machine Learning in Construction: From Shallow to Deep Learning, Developments in the Built Environment 6 (2021) 100045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dibe.2021.100045.
[26] N. Rane, Role of ChatGPT and Similar Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Construction Industry, Available at SSRN 4598258 (2023).
[27] R. Panchalingam, and K.C. Chan, A State-of-the-art Review on Artificial Intelligence for Smart Buildings, Intelligent Buildings International 13 (2021) 203-226. https://doi.org/10.1080/17508975.2019.1613219.
[28] T.D. Akinosho, L.O. Oyedele, M. Bilal, A.O. Ajayi, M.D. Delgado, O.O. Akinade, and A.A. Ahmed, Deep Learning in the Construction Industry: A Review of Present Status and Future Innovations, Journal of Building Engineering 32 (2020) 101827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2020.101827.
[29] S.A. Bello, L.O. Oyedele, O.O. Akinade, M. Bilal, J.M. Davila Delgado, L.A. Akanbi, A.O. Ajayi, and H.A. Owolabi, Cloud Computing in Construction Industry: Use Cases, Benefits and Challenges, Automation in Construction 122 (2021) 103441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2020.103441.
[30] B. Manzoor, I. Othman, S. Durdyev, S. Ismail, and M.H. Wahab, Influence of Artificial Intelligence in Civil Engineering toward Sustainable Development—A Systematic Literature Review, Applied System Innovation 4 (2021) 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi4030052.
[31] A.A. Khan, A.O. Bello, M. Arqam, and F. Ullah, Integrating Building Information Modelling and Artificial Intelligence in Construction Projects: A Review of Challenges and Mitigation Strategies, Technologies 12 (2024) 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/technologies12100185.
[32] I. Taboada, A. Daneshpajouh, N. Toledo, and T. de Vass, Artificial Intelligence Enabled Project Management: A Systematic Literature Review, Applied Sciences 13 (2023) 5014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13085014.
[33] F. Zhang, A.P.C. Chan, A. Darko, Z. Chen, and D. Li, Integrated Applications of Building Information Modeling and Artificial Intelligence Techniques in the AEC/FM Industry, Automation in Construction 139 (2022) 104289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104289.
[34] A. Banerjee, and R.R. Nayaka, A Comprehensive Overview on BIM-integrated Cyber Physical System Architectures and Practices in the Architecture, Engineering and Construction Industry, Construction Innovation 22 (2022) 727-748. https://doi.org/10.1108/CI-02-2021-0029.
[35] D.D. Eneyew, M.A.M. Capretz, and G.T. Bitsuamlak, Toward Smart-Building Digital Twins: BIM and IoT Data Integration, IEEE Access 10 (2022) 130487-130506. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3229370.
[36] Z. Fan, Z. Yan, and S. Wen, Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Sustainability: A Review of SDGs, Renewable Energy, and Environmental Health, Sustainability 15 (2023) 13493. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151813493.
[37] B.I. Oluleye, D.W.M. Chan, and P. Antwi-Afari, Adopting Artificial Intelligence for Enhancing the Implementation of Systemic Circularity in the Construction Industry: A Critical Review, Sustainable Production and Consumption 35 (2023) 509-524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spc.2022.12.002.
[38] D.-G.J. Opoku, S. Perera, R. Osei-Kyei, M. Rashidi, T. Famakinwa, and K. Bamdad, Drivers for Digital Twin Adoption in the Construction Industry: A Systematic Literature Review, Buildings 12 (2022) 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings12020113.
[39] P. Mêda, D. Calvetti, E. Hjelseth, and H. Sousa, Incremental Digital Twin Conceptualisations Targeting Data-Driven Circular Construction, Buildings 11 (2021) 554. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings11110554.
[40] A.A. Akanmu, C.J. Anumba, and O.O. Ogunseiju, Towards Next Generation Cyber-Physical Systems and Digital Twins for Construction, Journal of Information Technology in Construction 26 (2021). https://doi.org/10.36680/j.itcon.2021.027.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Progress in Energy and Environment

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















