Sensitivity Analysis of Hydrodynamic and Sediment Parameters Affecting Bed Morphology in Tidal Environments, and Potential Application on Soil
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/sea.5.1.4858Keywords:
Shallow water equation, sediment transport, bed morphology, Grass equation, Exner equationAbstract
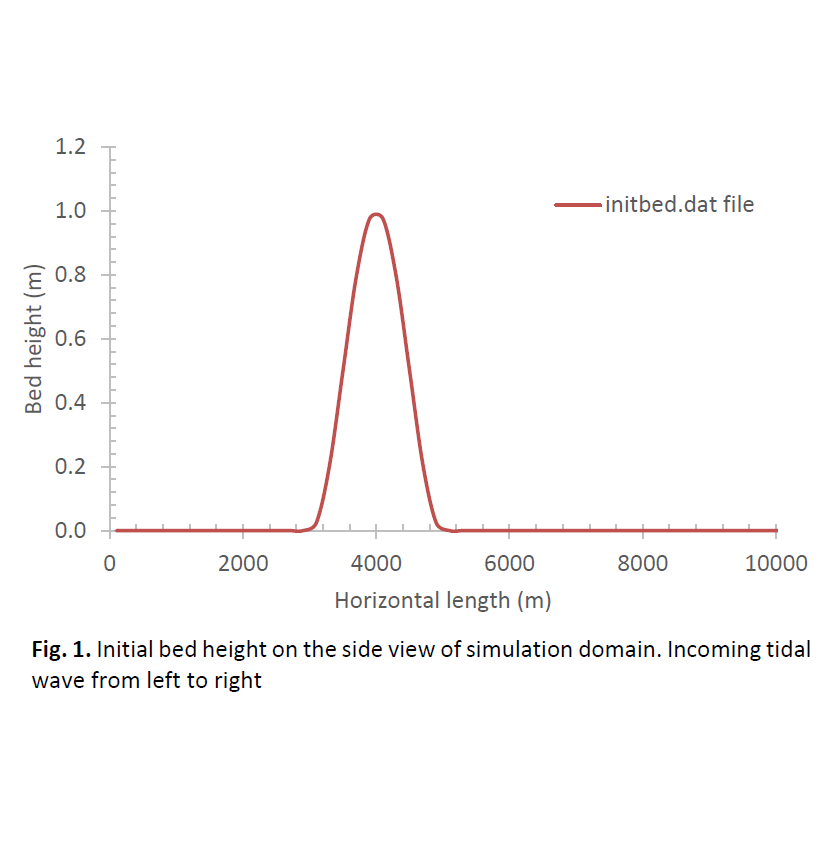
Comprehending sediment transport dynamics is crucial for forecasting morphological changes in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems, especially where hydrodynamic factors like tides or surface runoff markedly affect sediment redistribution. This research employs a one-dimensional (1D) numerical model that integrates the Saint-Venant shallow water equations with sediment transport equations, using the Exner equation for bed evolution and the advection-diffusion equation for suspended load. Bedload transport is characterized by the Grass equation, which models sediment flux as a function of depth-averaged velocity and an empirical coefficient (Ag) that incorporates a combined effects of many physical properties on sediment transport. Simulations were performed over diverse tidal ranges, durations, Grass coefficient, and bed friction coefficients (Cf) to evaluate their singular impacts on sediment dynamics. Results indicated that prolonged simulation durations and heightened tidal amplitudes exacerbated sediment redistribution and bedform flattening, signifying cumulative morphological changes over time. Elevated Grass coefficient and friction coefficient values substantially impacted bed stability, with high Ag values promoting sediment mobility and high Cf acting as a regulator of shear stress and reduce erosion intensity. Sensitivity analysis indicated that Ag is the most significant parameter influencing morphological change. These findings hold significant significance for agricultural soil erosion research, as analogous mechanisms of sediment displacement regulate both natural and managed systems. The coefficients for Grass and friction can be modified to reflect surface conditions, including vegetation cover and tillage methods on agricultural lands. This underscores the potential for interdisciplinary application of hydrodynamic sediment models to guide erosion control measures and sustainable land use planning. The study recommends extending the model to study and facilitating its practical application in erosion monitoring and agricultural management systems.