Recent Plant-Based Fertilization Approaches: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/fsat.5.1.6775Keywords:
Plant-based fertilizers, sustainable agriculture, nutrient management, fermented plant juice, inorganic fertilizerAbstract
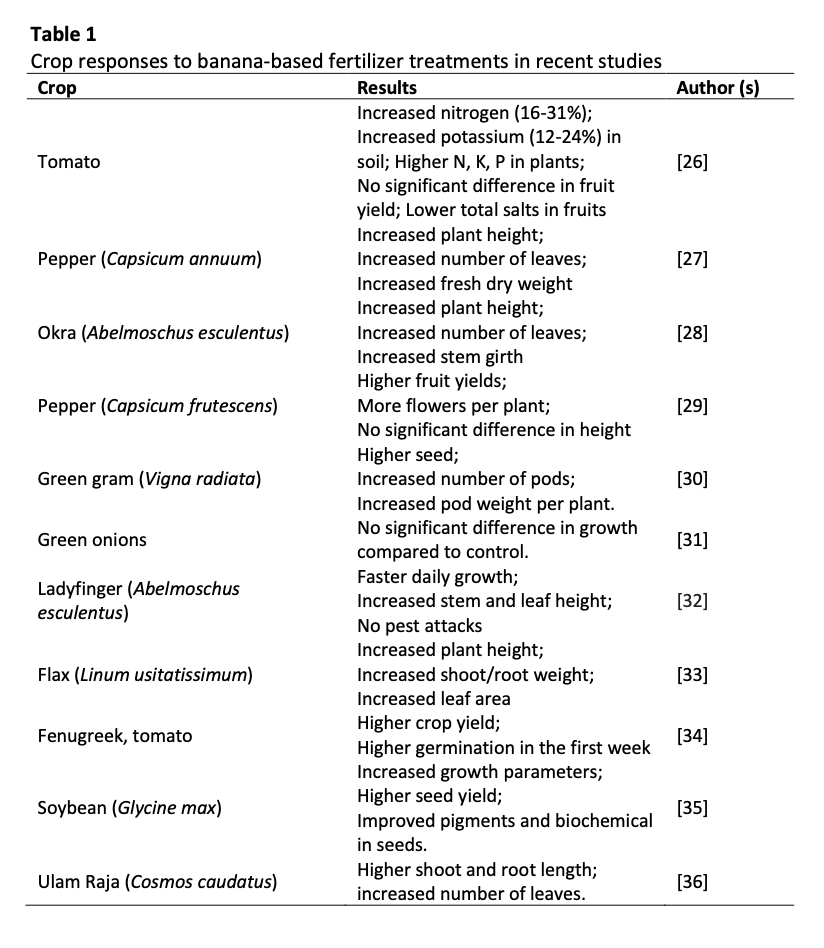
The reliance on inorganic fertilizers has been central to modern agriculture but has raised serious environmental and agronomic concerns, including soil degradation, nutrient imbalances, water contamination and greenhouse gas emissions. In response, plant-based fertilizers have gained attention as sustainable alternatives that enhance soil fertility, crop performance and ecological balance. This review synthesizes recent advances in plant-derived fertilizers, including duckweed, rice husk, fermented plant juice, sunflower residues and banana peels. These materials supply essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, while also improving soil microbial activity, nutrient retention and crop yield. Studies demonstrate benefits such as reduced nitrogen leaching with duckweed, enhanced soil enzyme activity with rice husk biochar, improved flowering and photosynthesis with fermented plant juice and high potassium contributions from sunflower and banana residues. Despite promising results, challenges remain regarding nutrient variability, slow release rates, standardization and economic feasibility, which limit large-scale adoption. Innovations such as microbial enrichment and nano-formulations are improving efficiency, but further long-term field trials are needed. This review highlights both the agronomic potential and limitations of plant-based fertilization, emphasizing their role in sustainable agriculture and future integration into climate-smart farming systems.