Integrating Fuzzy Maclaurin Symmetric Mean and DEMATEL Method for Water Management Strategies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/fwe.7.1.2537Keywords:
Fuzzy, Maclaurin Symmteric Mean, DEMATEL, water management strategiesAbstract
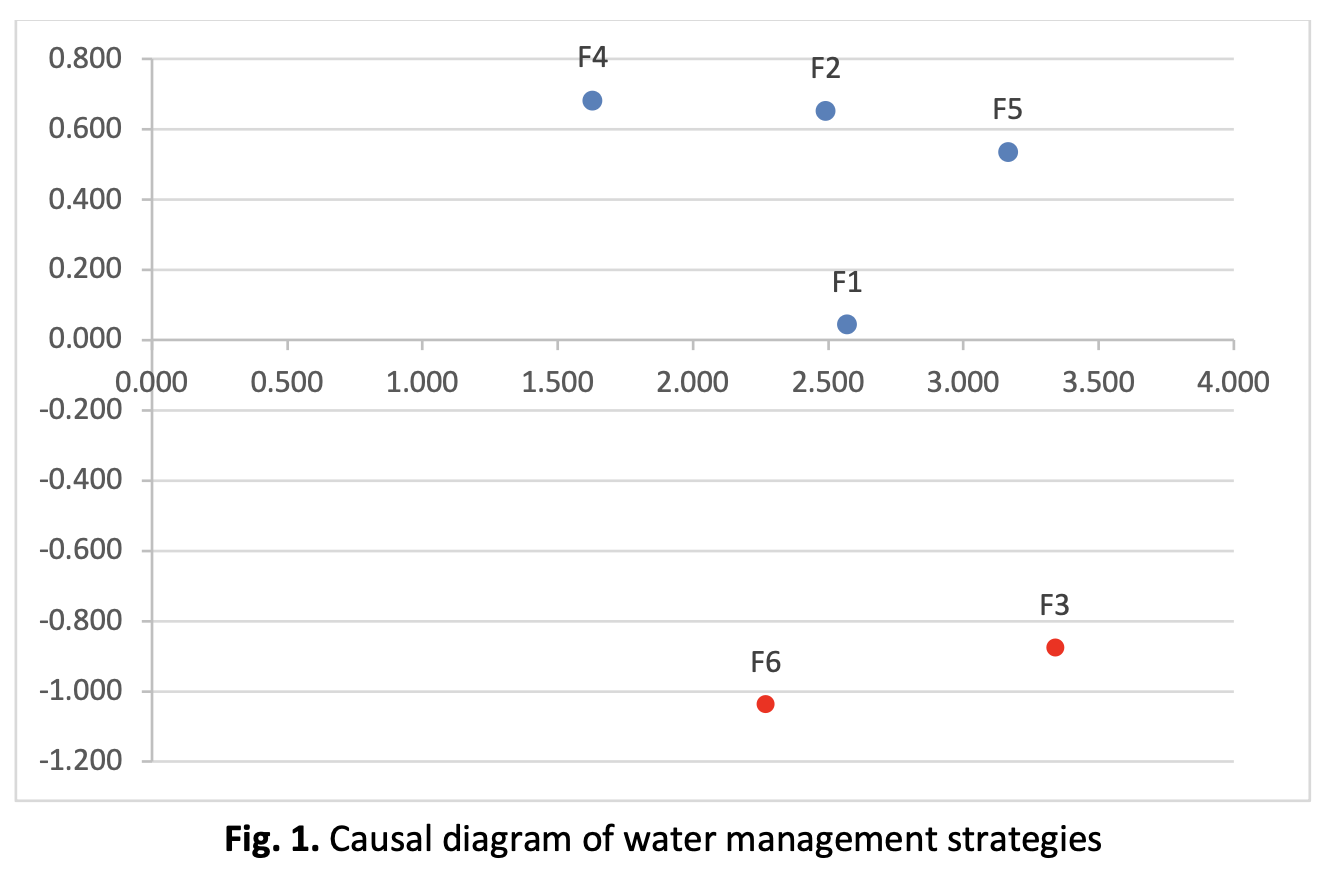
Water management is a critical challenge faced globally, as efficient management of this vital resource is essential for sustainable development. This study aims to identify and analyze key factors influencing water management strategies, specifically focusing on water availability, water quality, environmental, population growth, pollution & contamination and technological factors. To achieve this, the study develops an integrated decision-making framework combining the fuzzy Maclaurin Symmetric Mean (MSM) and Decision-Making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) methods. The study is conducted under fuzzy environment as accounting for uncertainty in decision-making and MSM is used to aggregate multiple data. DEMATEL is then applied to model the causal relationships among the factors. The case study results highlight the significant interdependencies between population growth, water availability and pollution with technological factors identified as crucial in addressing challenges related to water quality and contamination. The findings demonstrate that the integrated framework provides valuable insights into the prioritization and optimization of water management strategies, offering a comprehensive approach to tackle the complex and dynamic challenges of water resource management. This research contributes to the development of more analytical and effective solutions for sustainable water management in a rapidly changing environment.