CFD Analysis of Flow Mixing in a Pipe with Two Inlets
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/afhme.7.1.1319aKeywords:
T-junction pipe, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), Pressure drop, Velocity distribution, Outlet diameter, Turbulent mixingAbstract
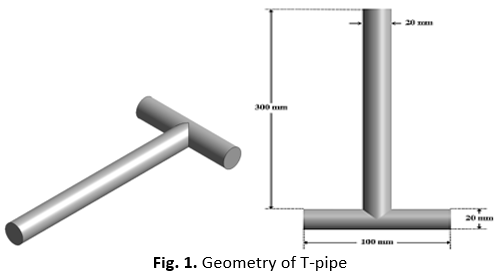
The reasons for this importance are that mixing in T-junction pipe systems is essential in many industrial applications, but the influence of the diameter on mixing behaviour has not been well documented. Therefore, this paper discusses the influence of three outlet diameters on velocity distribution, pressure drop and mixing performance using the computational fluid dynamics approach. A two-inlet T-junction was modelled using ANSYS. Steady-state turbulent flow was simulated using the RANS k-ω SST model for three outlet diameters, namely 20 mm, 15 mm, and 10 mm. A Grid Independence Test was carried out to ensure the accuracy of the meshes. Smaller outlet diameters increase the downstream velocity and turbulence intensity, which strengthens the shear layers and enhances mixing. Consequently, these conditions also result in higher pressure losses near the junction. The strongest mixing was obtained with the 10 mm outlet. However, this configuration also produced the greatest pressure drop. Therefore, the outlet diameter is a critical parameter that governs both the mixing effectiveness and the overall hydraulic performance of T-junction flows.