Determinants of the Sustainable Business Performance of Women Entrepreneurs in the Developing World Context: The Mediating Influence of Self-Efficacy
Keywords:
Sustainable business performance, women entrepreneurs, self-efficacy, mediation effectAbstract
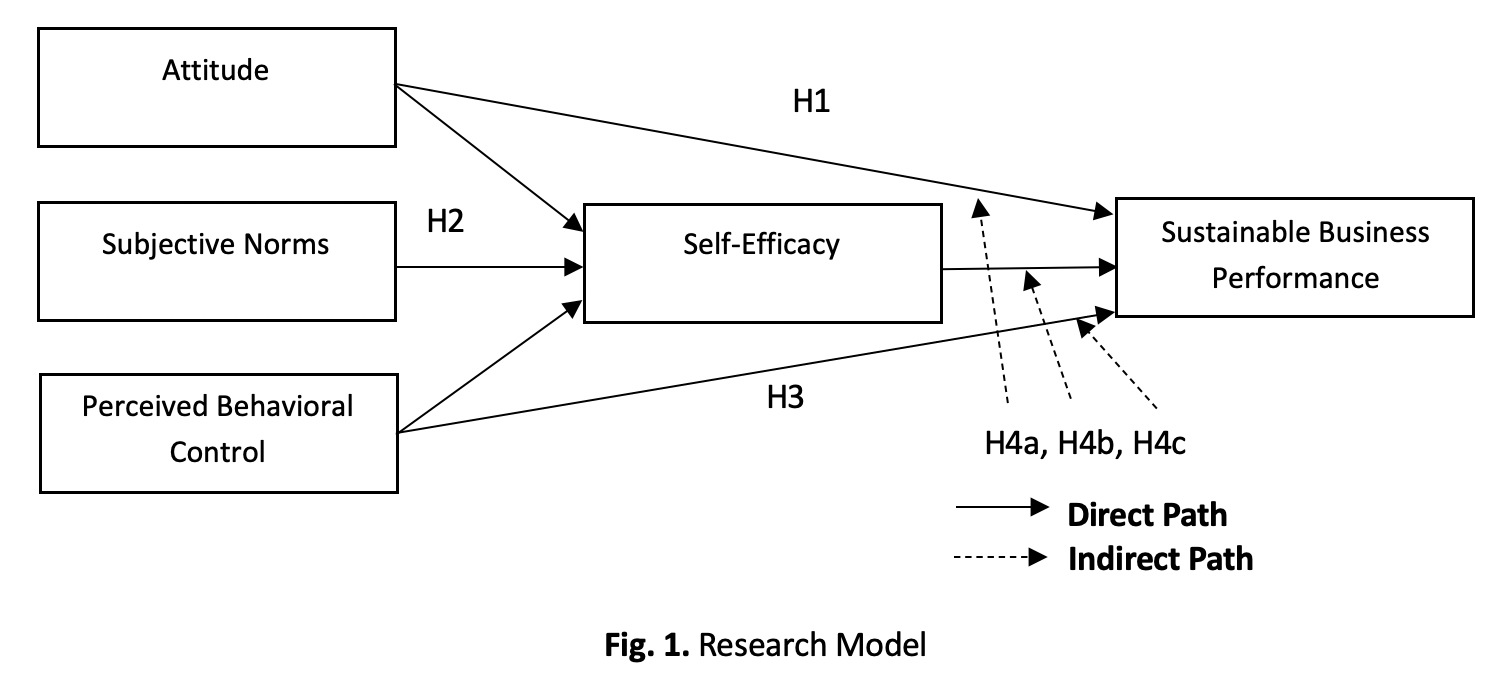
By implementing sustainable practices, businesses can ensure prosperity, stability, and a better quality of life. Achieving sustainable prosperity requires the harmonious management of social, environmental, and cultural aspects. The study's objective is to examine the influence of attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioural control, and self-efficacy on the sustainable business performance of women entrepreneurs. Second, it is to examine the mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationships between attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioural control, and sustainable business performance. This study employs a quantitative approach, utilizing survey methods as its research methodology. The study sample comprises 400 respondents selected from four states (i.e., Selangor, Kuala Lumpur, Negeri Sembilan, and Johor) in Peninsular Malaysia, who were selected using a combination of cluster and purposive sampling techniques. The data were analyzed using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and structural equation modeling (SEM) with the AMOS 29 program. The findings discovered that attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioural control, and self-efficacy significantly influence the sustainable business performance of women entrepreneurs. The second finding showed that self-efficacy significantly mediates the relationships between attitude, subjective norms, and sustainable business performance of women entrepreneurs. Conversely, self-efficacy does not mediate the relationship between perceived behavioural control and sustainable business performance. Theoretically, this study helps to validate and improve the application of the theory of planned behaviour (TPB) and delivers new insights for the entrepreneurial literature. Most empirical studies have focused on financial performance measurement in the Western context, with a limited study population that requires further explanation.