Strengthening Waqf Management in Malaysian Public University: An Exploratory Analysis of Issues and Challenges
Keywords:
Waqf management, issues and challenges, higher education, qualitative analysis, Kawakita Jiro MethodAbstract
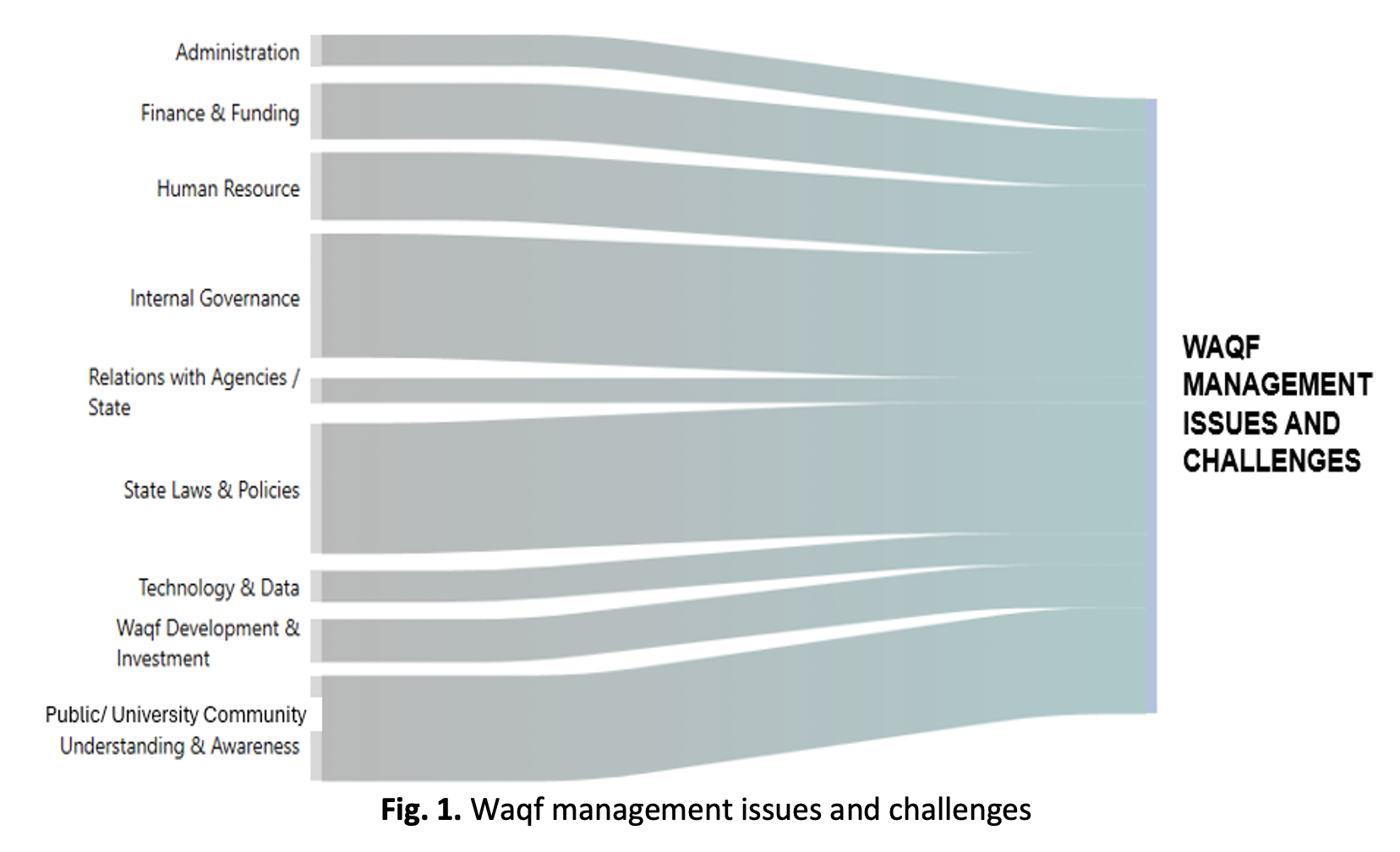
This study explores the key issues and challenges in waqf management within Malaysian public university, aiming to strengthen governance frameworks and enhance operational effectiveness. Despite waqf’s historical significance as a sustainable instrument for social and educational development, its administration in higher education remains constrained by structural, financial, and regulatory complexities. Employing the Kawakita Jiro (KJ) method, a qualitative and participatory analytical approach, data were collected through five focus group discussions involving practitioners directly engaged in university-level waqf management across Malaysian states. The KJ method facilitated the systematic organization and clustering of unstructured qualitative data, while subsequent content analysis using ATLAS.ti version 23 enabled the identification of recurring themes. Findings reveal that the most prominent challenges relate to internal governance, state law and policies, and public or university community awareness, followed by human resource and financial constraints. Less frequent but significant issues include administration, technology and data management, relations with agencies, and waqf development and investment. Collectively, these findings indicate that waqf management challenges are multidimensional and interdependent across institutional, legal, and socio-technical domains. Theoretically, this study contributes to the waqf governance literature by demonstrating how internal institutional mechanisms interact with legal and socio-political contexts to shape waqf outcomes in higher education, while also highlighting the effective application of the KJ method as a systematic framework for analysing managerial and operational challenges. Practically, the study underscores the importance of policy reform, capacity building, technological innovation, and stakeholder engagement to enhance the sustainability and impact of waqf in higher education.