Microsleep Digital Twin for Fleet Safety: A Data-Driven Framework for Modelling Driver Fatigue in Malaysian Urban Mobility
Keywords:
Microsleep detection, digital twin simulation, fleet safety, driver fatigue, smart mobility, smart cityAbstract
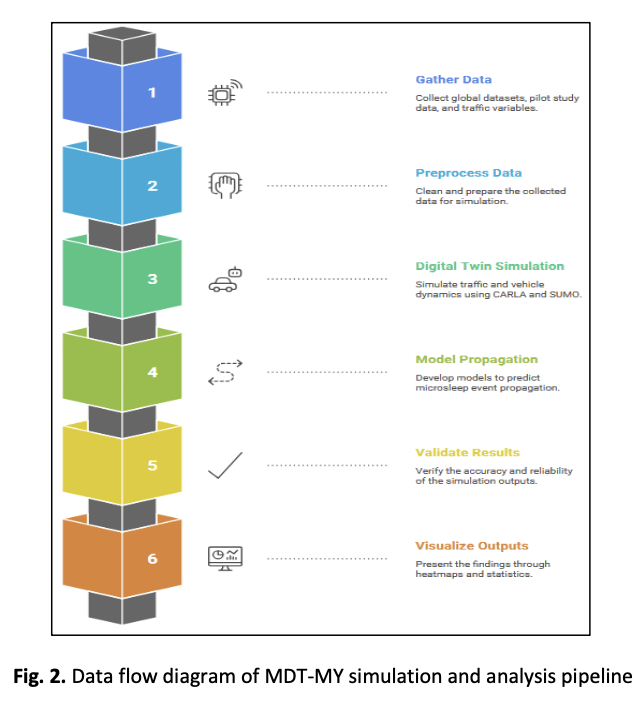
Driver fatigue and microsleep remain under-addressed contributors to fleet-related incidents in Malaysian urban mobility networks. Existing studies primarily focus on individual drowsiness detection, with limited attention to how fatigue-induced events propagate across interconnected fleet operations. This study proposes the Malaysian Microsleep Digital Twin (MDT-MY), a modelling framework designed to quantify both individual fatigue risk and its system-level ripple effects on near-miss probability, congestion, and schedule reliability. The framework integrates global fatigue indicators with locally calibrated telemetry from a pilot sample of 15 shuttle drivers a dataset appropriate for simulation calibration though not intended for broad generalisation. Using agent-based and probabilistic modelling, the digital twin simulates how microsleep events escalate into network disruptions and evaluates mitigation strategies. Results show that short microsleep episodes significantly increase near-miss likelihood and operational delays, while micro-rest and AI-assisted alert interventions reduce propagated risk. MDT-MY demonstrates the importance of shifting from isolated detection approaches toward system-level modelling, offering a data-informed foundation for improving safety under Malaysia’s Road Safety Plan 2022–2030.