Enhanced Model Compression for Lip-reading Recognition based on Knowledge Distillation Algorithm
Keywords:
Lip-reading, model compression, deep learning, knowledge distillationAbstract
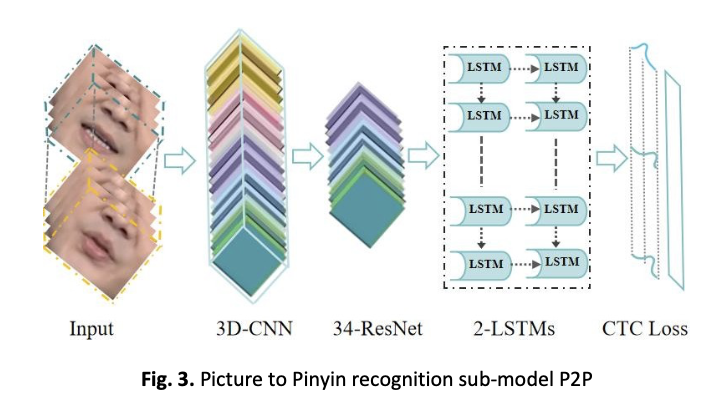
Lip-reading is the process of understanding what a speaker is saying by observing changes in the speaker's mouth. With the development of computer vision and natural language processing technology, lip-reading recognition technology has been paid more and more attention and applied. Especially in recent years, deep learn-based lip-reading recognition technology has made great progress, and the lip-reading model is becoming increasingly complex, requiring a lot of computing resources, and it is difficult to apply to portable mobile devices directly. The lip-reading recognition model LipPC-Net proposed in this paper is built with a large Chinese lip-reading data set based on Chinese phonetic rules and grammatical features and consists of two main parts: the P2P sub-model and the P2C sub-model. The P2P sub-model is a model for identifying pinyin sequences from pictures, while the P2C sub-model is a model for identifying Chinese character sequences from pinyin. However, due to China's rich and ambiguous language features, its training and optimization rely on a graphics processor (GPU), which has high computing power and storage space requirements, so staying in the theoretical research stage and large-scale promotion and application is difficult. To realize the transformation of scientific research results as soon as possible, highlight the universality of the lip-reading model under the intelligent environment, and solve the problem of how to embed the lip-reading model into the mobile terminal with limited computing and storage capabilities, this paper proposes three knowledge distillation compression algorithms to complete the compression of the Chinese character sequence output by the model. They are an offline model compression algorithm based on multi-feature transfer (MTOF), an online model compression algorithm based on adversarial learning (ALON), and an online model compression algorithm based on consistent regularization (CRON). MTOF can solve the problem of single migration features, ALOF middle layer feature mutual learning is ignored, CRON can solve the problem of decision boundary fuzzy features are ignored, through the three compression algorithms to fit and learn the transformation between different features, so that portable mobile terminals with limited hardware resources can carry this model. Then, realize the practical application value of assisting the communication of the deaf and mute.