Chlorophyll Intensity Forecasting in Diverse Plant Species: Advancing with Enhanced Convolutional Neural Networks
Keywords:
Chlorophyll intensity, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), prediction, leaf spectra, hybrid, Mean Square Error (MSE)Abstract
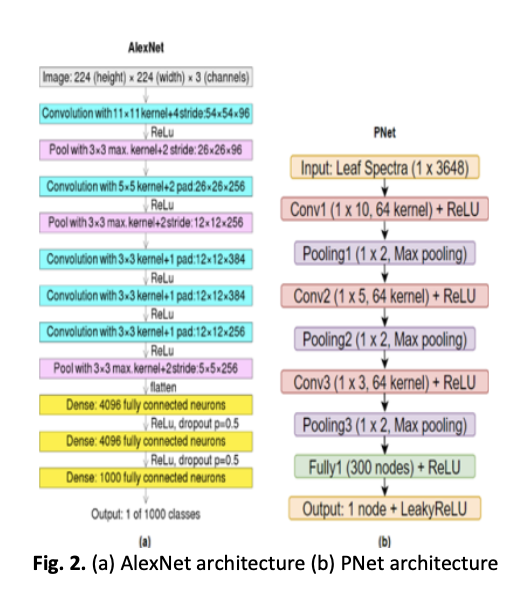
Chlorophyll pigment plays a crucial role in photosynthesis by absorbing and harnessing light energy, ultimately supporting the plant's overall health and growth by providing essential nutrients. A convenient assessment of chlorophyll content is essential in smart management agriculture. It is very important to measure chlorophyll intensity in a leaf accurately as it can indicate the plant health status in terms of its growth, photosynthetic capacity, and nutritional stress. Several attempts have been made to implements computer vision to enhance the precision agriculture techniques However, recent literatures about chlorophyll intensity prediction of various plant species using non-destructive methods are limited and yet existing methods for chlorophyII intensity forecasting are time-consuming. Hence, a rapid and straightforward convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithm was proposed to predict chlorophyll intensity of various plant species based on leaf reflectance spectra. The datasets were taken from ANGERS Leaf Optical Properties Database (2003). The proposed model consists of Hybrid CNN as a feature extractor and Support Vector Regression (SVR) network as a predictor. Hybrid CNN was designed by modifying the architectures of AlexNet and PNet. The performance of Hybrid CNN with SVR (CNN-SVR) was also compared with AlexNet, PNet, and SVR. Hybrid CNN exhibits superior performance when compared to established models, including AlexNet, PNet, and standalone SVR. Notably, the mean square error values for training and testing datasets stand at 0.1558 and 1.149, respectively. This substantiates the model's efficacy in predicting chlorophyll intensity accurately, underscoring its potential utility in advancing precision agriculture techniques.