Risk Assessment Fuzzy-FMEA for the Prevention and Control of COVID-19 at Sarawak Longhouses
Keywords:
COVID-19, FMEA, artificial intelligence, multi-criteria decision making, Mathematical programming, integrated approachAbstract
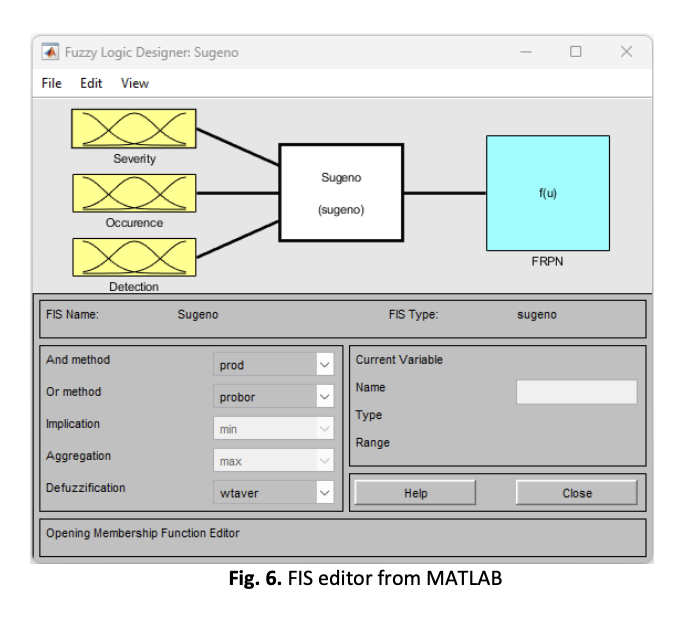
The COVID-19 outbreak causes great concern due to the high rates of infection and the large number of deaths worldwide. This paper presents a risk assessment Fuzzy-FMEA for the prevention and control of COVID-19 at Sarawak longhouses. The paper also provides a comprehensive review study on the transmission potentials, effects, and causes of COVID-19, which emphasize Artificial Intelligence (AI), Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM), integrated approaches, and mathematical programming with Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA). The spreading of COVID-19 can be controlled and prevented by implementing the FMEA method by considering each failure mode's severity, occurrence, and detection rating via the Risk Priority Number (RPN) value. However, FMEA alone cannot provide a precise risk evaluation as the generated RPN might be unreliable in real-life applications. Recent research shows that the limitation of conventional FMEA can be tackled by aggregating it with other approaches. In conclusion, FMEA with a combination of fuzzy methods is a great integration in order to conduct a risk assessment to prevent and control infectious diseases, which in this paper is focused on COVID-19 incidences.