Facial Expression Recognition using Stretchable Sensor and Multilayer Feedforward Backpropagation Neural Network
Keywords:
Facial expression recognition, stretchable sensor, multilayer feedforward backpropagation algorithm, neural networkAbstract
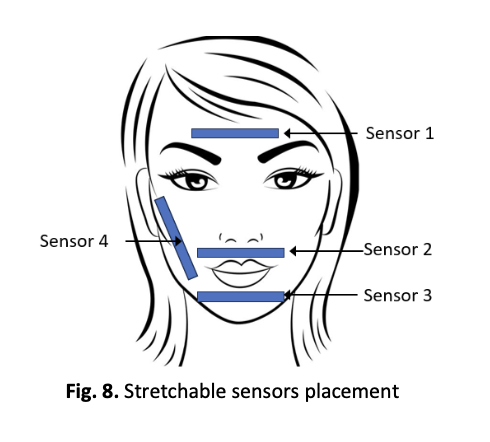
Facial expression recognition plays a crucial role in enabling natural human–computer interaction, emotion identification systems and finds diverse applications in healthcare, security, marketing and social robotics. Traditionally, facial expression recognition relies on vision-based systems, which are often limited by sensitivity to lighting and pose variations, occlusions and high computational cost. Therefore, this study proposes a facial expression recognition system based on stretchable sensor data for controlling the movement of a robotic hand. Stretchable sensors are capable of conforming to complex and dynamic surfaces such as human skin while maintaining sensing accuracy under deformation. In this study, four stretchable sensors are placed on the forehead, upper lip, lower lip, and right cheek. The sensors are interfaced with an Arduino Mega 2560 microcontroller for data acquisition. Statistical features including mean, root mean square (RMS), variance and standard deviation are extracted and used to train a multilayer feedforward backpropagation neural network algorithm in classifying four expressions: neutral, happy, sad, and disgust. The trained model outputs are mapped to control four servo motors attached to the robotic hand’s fingers and wrist, producing peace, thumbs-up, fist gestures, and wrist rotation. The validation results demonstrate that the proposed system achieved 100% accuracy in the training phase but a significantly low accuracy of 25% in the testing stage. This shows that further improvement is needed to improve the stretchable sensor-based facial expression recognition system .