Enhanced Tribological Performance of Canola Oil-Based Nano-Cutting Fluids with Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) Nanoparticle Additives under the Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) Method
Keywords:
MQL, Canola Oil, h-BN, Nano-Cutting FluidAbstract
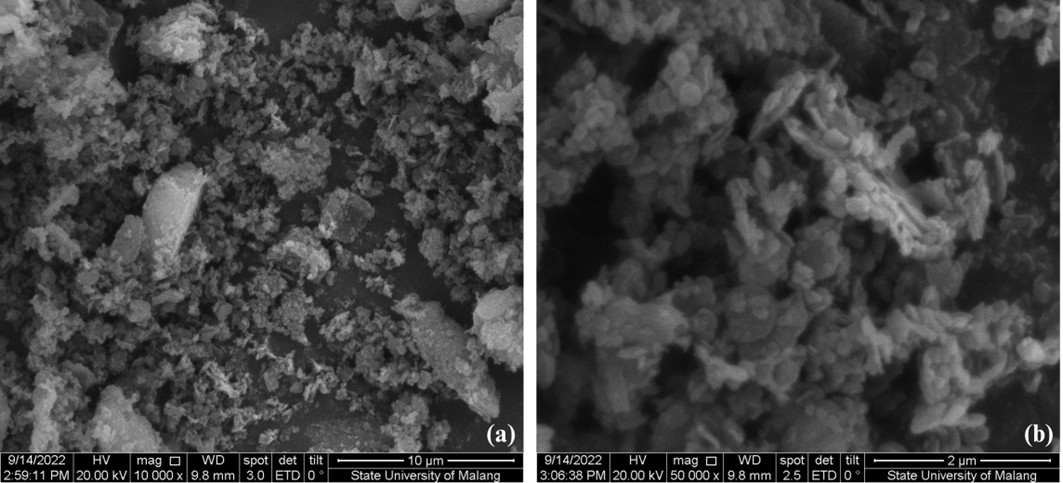
The modern manufacturing industry faces the challenge of improving product quality while reducing the environmental impact of using mineral oil-based cutting fluid. Minimum Quantity Lubrication (MQL) has emerged as an eco-friendly alternative. However, its thermal and tribological efficiency under intensive cutting conditions remains suboptimal. This study introduces canola oil-based nano-cutting fluids with hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) nanoparticle additives to enhance thermal and tribological performance in MQL-assisted machining. Three formulations with varying concentrations of h-BN nanoparticles (0.1, 0.15 and 0.2 wt%) were synthesized and experimentally evaluated in the CNC milling of AISI 1045 using the MQL method. The experimental evaluation included testing thermophysical properties, such as density, dynamic viscosity, thermal conductivity, rheological properties, and tribological performance through measurements of cutting temperature, tool wear, and surface roughness. The results showed that adding h-BN nanoparticles increased density and viscosity, with the optimum thermal conductivity value reached at a fraction of 0.15 wt%. Tribologically, the nano-cutting fluid containing 0.15 wt% h-BN achieved the best performance, recording the lowest cutting temperature (35.43 °C), the least tool wear (0.120 mm²), and the smoothest surface finish (0.86 µm). These improvements are attributed to the synergistic effects of tribo-film formation and the enhanced thermal conductivity provided by the h-BN nanoparticles, outperforming dry cutting, Dromus, and pure canola oil. This study confirms the synergistic effect of biodegradable canola oil and h-BN in enhancing eco-sustainable precision machining, contributing to green manufacturing aligned with Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 12.