Study and Performance Analysis using RSA Algorithm of Cryptography in QR Code
Keywords:
Cryptography, data security, encryption, QR code, RSA algorithmAbstract
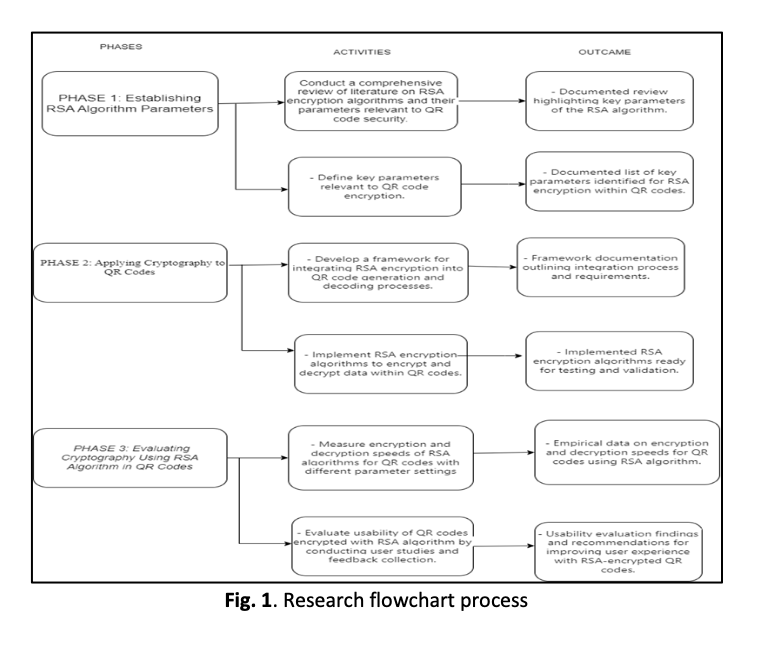
The increasing reliance on Quick Response (QR) codes as a medium for data exchange across various domains has heightened concerns regarding information security. This study examines the application of the Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) cryptographic algorithm in conjunction with QR codes to enhance the confidentiality and integrity of transmitted data. The objectives of the research are threefold: to define the encryption and decryption parameters of RSA, to implement RSA within QR code structures, and to evaluate its performance in terms of computational efficiency. An experimental methodology was employed, utilizing RSA key lengths of 1024, 2048, and 3072 bits, alongside variable data sizes ranging from 10 to 60 words, to assess encryption and decryption times. The experimental findings indicate that larger RSA key sizes significantly strengthen security, albeit at the expense of longer decryption durations, while variations in data size exert only minimal influence on performance. The study affirms the suitability of RSA for securing QR code applications, while also emphasizing the necessity of achieving an equilibrium between cryptographic strength and system performance. The insights derived from this work provide a valuable reference for researchers, developers, and security practitioners engaged in the design and implementation of secure QR code systems. This study’s novelty lies in its experimental and statistical evaluation of RSA integration within QR codes, employing regression and T-test analyses to assess performance across multiple key and data sizes. Unlike previous conceptual works, the results identify key size as the primary factor affecting efficiency, establishing a clear balance between security strength and computational performance.