The Impact of Routing Protocol in Green IoT Environment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/feel.2.1.112Keywords:
Internet of things, network simulator, energy efficiency, routing protocol, wireless sensor networkAbstract
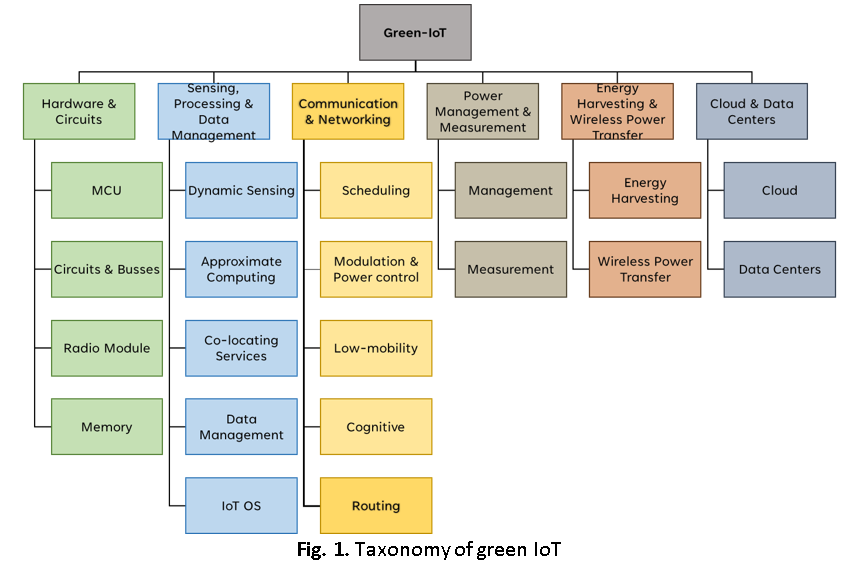
Technology is rapidly evolving to better daily human existence and directly impacts the earth's resource use. Reducing energy usage reduces carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions into the atmosphere, which can have negative consequences for the environment and human health. Achieving green Internet of Things (IoT) requires striking a balance between quick data transmission and economical energy consumption. The wireless sensor, part of the IoT system, is responsible for operating continuously without data delay. As a result, most wireless sensors collect raw data and transfer packets to another physical device, which will be evaluated later. Even though the sensors must still understand the routing topology on their own, the energy used to transport the packet to its destination can be reduced. Researchers have used various methods to reduce energy consumption, including alternative hardware and power management. Therefore, this study aims to see how using different types of routing protocols can impact energy consumption. The study was conducted using modelling and simulation to reduce variables influencing the result, such as signal strength, the earth's topography, and weather. The energy consumption can be viewed in detail using the NETSIM network simulator. Several topologies were designed to observe Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector (AODV) and Routing Protocol for Low-Power and Lossy Networks (RPL) energy consumption. The observation includes the energy consumption by the wireless sensor during establishing the connection, sending the packet, on standby and idling. Several results can be concluded during the end of the study. RPL consume a greater amount of energy during establishing a connection, while over a certain period, AODV consumes more energy when maintaining the connection. However, AODV still consumed a smaller amount of energy in a topology where wireless sensors were placed close to each other. Hence, the selection of routing protocol is essential as it can impact energy consumption, which has a major impact on achieving green IoT.