Debt Management Practices among Youth in Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jarmm.1.2.1222Keywords:
Debt management, Youth, Financial Literacy, Malaysia, Peer Influence, Parental Influence, Spending Habits, Attitude toward debtAbstract
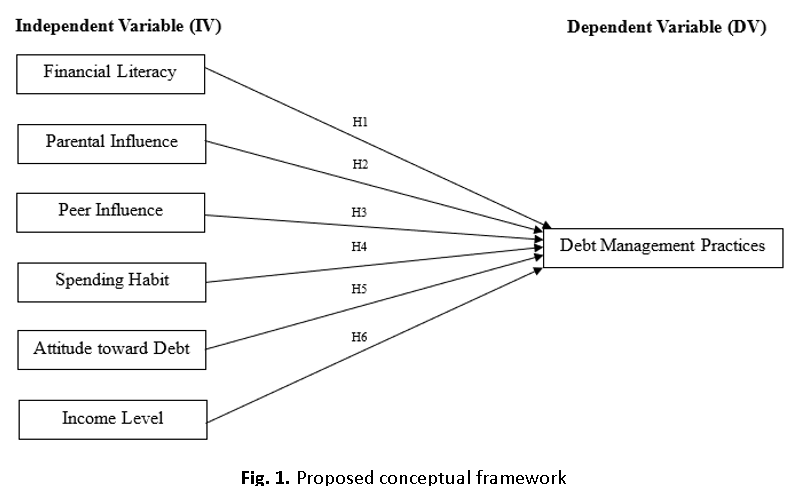
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the debt management practices among youth in Malaysia. The analysed independent variables are financial literacy, parental influence, peer influence, spending habits, attitude toward debt, and income level. This research used both Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA) and Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB) to evaluate the relationship between independent variable and debt management practices. Non probability purposive sampling method was used in this study to collect the data by distributing questionnaires to target respondents. IBM SPSS Statistics Version 27.0 software was used in this research to analyse the data collected. A total 190 responses were collected from youth residing in Malaysia. The research findings found that financial literacy, peer influence, attitude toward debt, and income level has a significant relationship towards debt management practices, while parental influence and spending habits has no significant relationship with the debt management practices. This study will provide a better understanding on factors affect an individual’s debt management practices and promote a good debt handling skill. This study suggests that future research may investigate more variables, including employment status, self-efficacy, and interest rates. Furthermore, study might be expanded to various geographical regions beyond Malaysia and encompass a broader demographic, including populations beyond the youth demographic.