Exploring the Influence of Family on School Dropouts among Indian Students from the B40 Group in Shah Alam District
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jarsbs.39.1.1227Keywords:
Students’ dropout, Indian community, B40 familyAbstract
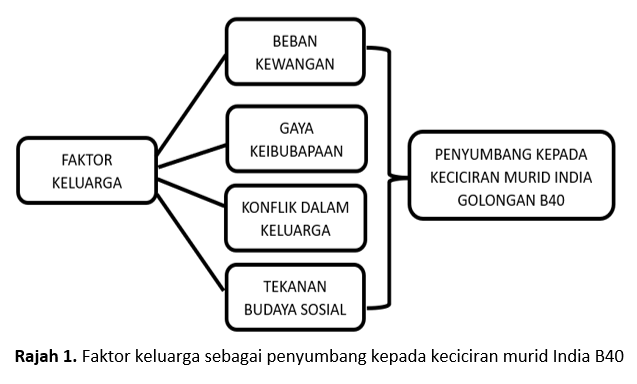
The issue of school dropouts among Indian students deserves attention, particularly those from low-income households (B40). Various factors contribute to the dropout rates among Indian students. This effort seeks to explore family influences with school dropouts among B40 Indian students in the Shah Alam district, identify the most dominant factor leading to dropouts, and propose preventive measures to improve current practices in addressing and reducing dropout rates. The study was conducted in several locations in Shah Alam, involving five Indian students from B40 families who had dropped out of secondary school, aged between 14 to 18 years, and sharing similar characteristics. This qualitative study utilized interviews, observations, and document analysis. The findings identified four key factors: financial burden, parenting style, family conflict, and cultural and social pressure. Among these, financial burden emerged as the most dominant factor contributing to dropouts among B40 Indian students in Shah Alam, closely linked to the other contributing factors. Several preventive recommendations have been put forward to address and reduce dropout problems among Indian students caused by family factors.