Factors Influencing the Intention to Use Digital Banking Services among Consumers in Perak, Malaysia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/jarmm.2.1.113Keywords:
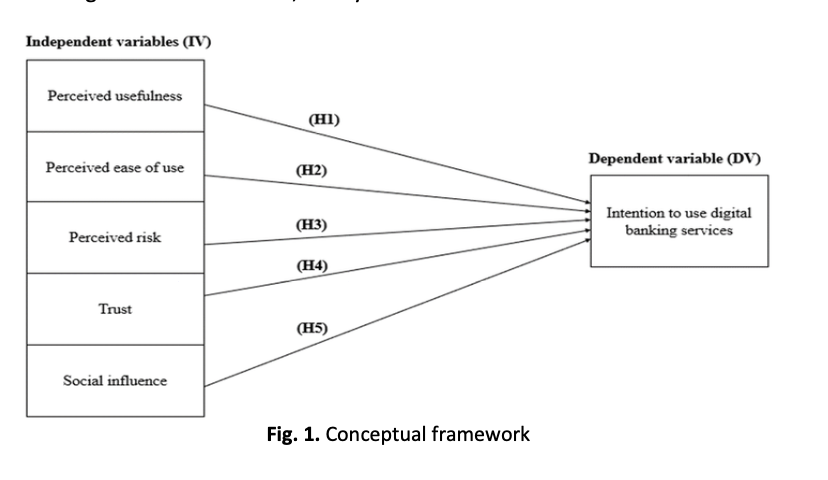
Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived risk, trust, social influenceAbstract
Digital banking services include all the traditional banking services that are available 24/7 on mobile devices, computers, and compatible smart devices, without the need for a customer’s presence in the bank branches. However, the adoption of digital banking services is still low among Malaysians as compared to other nations. The purpose of this study is to examine the factors influencing the adoption of digital banking services among consumers in Perak, Malaysia. The study analyses the factors which consist of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived risk, trust, and social influence. This study uses the Theory of Technology Acceptance Model, Extended Technology Acceptance Model, and Theory of Planned Behaviour to study the relationship between the independent variables and dependent variable. Additionally, the research’s data was collected through a questionnaire survey which was distributed by using the approach of purposive sampling. A total of 150 completed surveys collected from the consumers in Perak, Malaysia. Based on this study which highlighted that the two significant predictors of the consumers’ intention to adopt digital banking were perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness. This indicated that digital banking would be more likely to be adopted by the consumers when it satisfied their expectations in terms of user-friendly and beneficial whereas other variables namely perceived risk, trust, and social influence had less significant impact on the adoption of digital banking services. The implications of this study was that digital banking providers should prioritize digital banking’ usage and the benefits that consumers can gain to attract more adoption. As perceived risk, trust, and social influence were less influential, additional factors could be explored by the future researchers to be able to better understand what encourages the adoption of digital banking. Thus, new motivators could be unlocked which help in improving the adoption rate. The finding of this study can bring contribution to the field of digital banking research since there was limited studies on the intention to adopt digital banking services, specifically in Perak, Malaysia. Hence, it is advisable to conduct a comparison study in order to assess the adoption of digital banking services among consumers in Perak, Malaysia.