Attitudinal Intention of using Pragmatic Artificial Intelligence on Robotic Waiters in a Restaurant Services
Keywords:
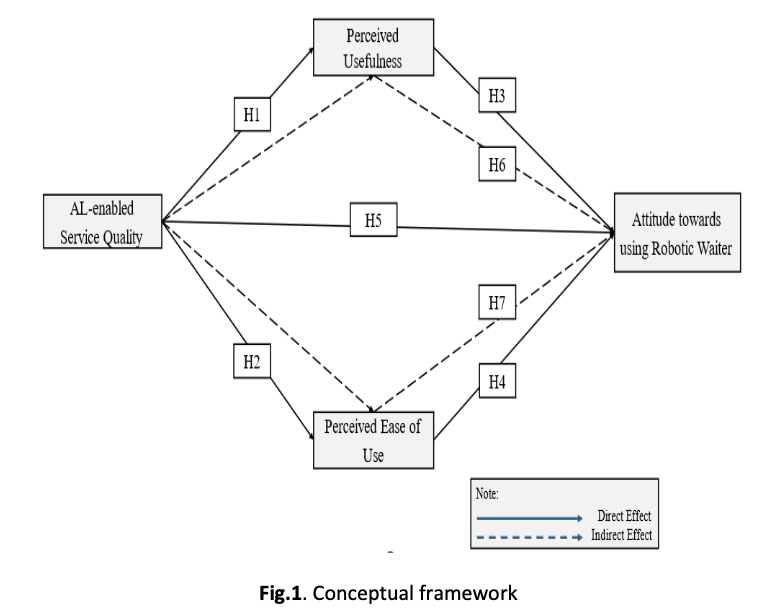
AI-Enabled service quality, perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, attitude towards using, robotic waiterAbstract
The rapid adoption of AI in the hospitality industry has changed the way services are provided, especially due to a shortage of workers in the restaurant sector. Robotic waiters have emerged as a potential solution to operational issues, but how clients perceive and accept this type of technology remains unclear. The goal of this research is to examine the factors influencing consumers' intentions to use robotic waiters, using the established technology adoption model (TAM) and digital self-determination (DSD). A quantitative research methodology was used with data collected from 267 restaurant clients in Kuala Lumpur. SPSS has been used for descriptive statistics and exploratory factor analysis, and SEM AMOS has been used to test hypotheses and investigate mediation. The findings show that AI-enhanced service quality has a considerable positive impact on perceived usefulness and ease of use, both of which play an important role in determining consumer perceptions. Perceived usefulness was identified as a major mediator between service quality and attitudes, although perceived ease of use had no mediation effect. This study discovered that boosting the quality and perceived value of AI-enabled services can foster positive consumer sentiments, allowing for the effective integration of robotic waiters in restaurants. The findings provide restaurant managers with valuable strategies by demonstrating how perceived usefulness might lead to acceptance. They also help us understand how technology is used in service contexts. The study emphasizes the potential of robotic waiters to alleviate labour shortages while increasing customer satisfaction.