Indoor Self-Aware Positioning Robot using Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Keywords:
Autonomous robot, BLE, indoor positioning system, obstacle avoidance, RSSI, trilateration, fingerprinting, ESP32Abstract
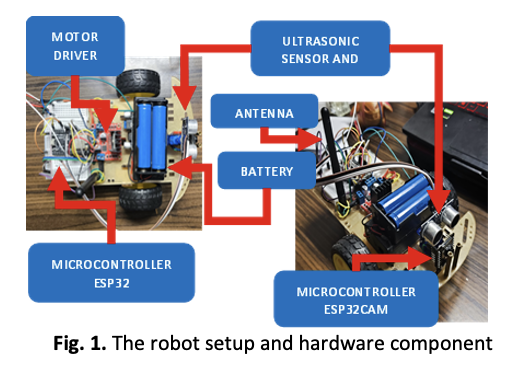
This paper presents the development of an autonomous indoor mobile robot utilizing Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology for self-aware localization and navigation. The proposed system features a distributed hardware architecture, employing a standard ESP32 for motor control and BLE signal processing, alongside an ESP32-CAM to host a real-time web-based Graphical User Interface (GUI). Localization is achieved through Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) trilateration and fingerprinting, enhanced by a Kalman filter to mitigate multipath interference and signal noise. Experimental results demonstrate a positioning accuracy of 74.27% in static conditions and 72% during autonomous movement. While the ultrasonic sensor system achieved a 100% success rate in detecting static obstacles of varying materials (cloth, glass, cardboard) within a 25 cm range, the reliability of the obstacle avoidance maneuver was limited (20% success rate) due to orientation drift inherent in the open-loop motor control mechanism. The system offers a scalable, cost-effective prototype for indoor navigation with potential applications in environments such as warehouses and smart buildings, subject to further domain-specific validation.