Digital Twin Integration for Photovoltaic–Battery Energy Storage Systems: A Systematic Review of Architectures, Intelligent Control and Deployment Pathways
Keywords:
Digital Twin, Renewable energy, Energy management systemAbstract
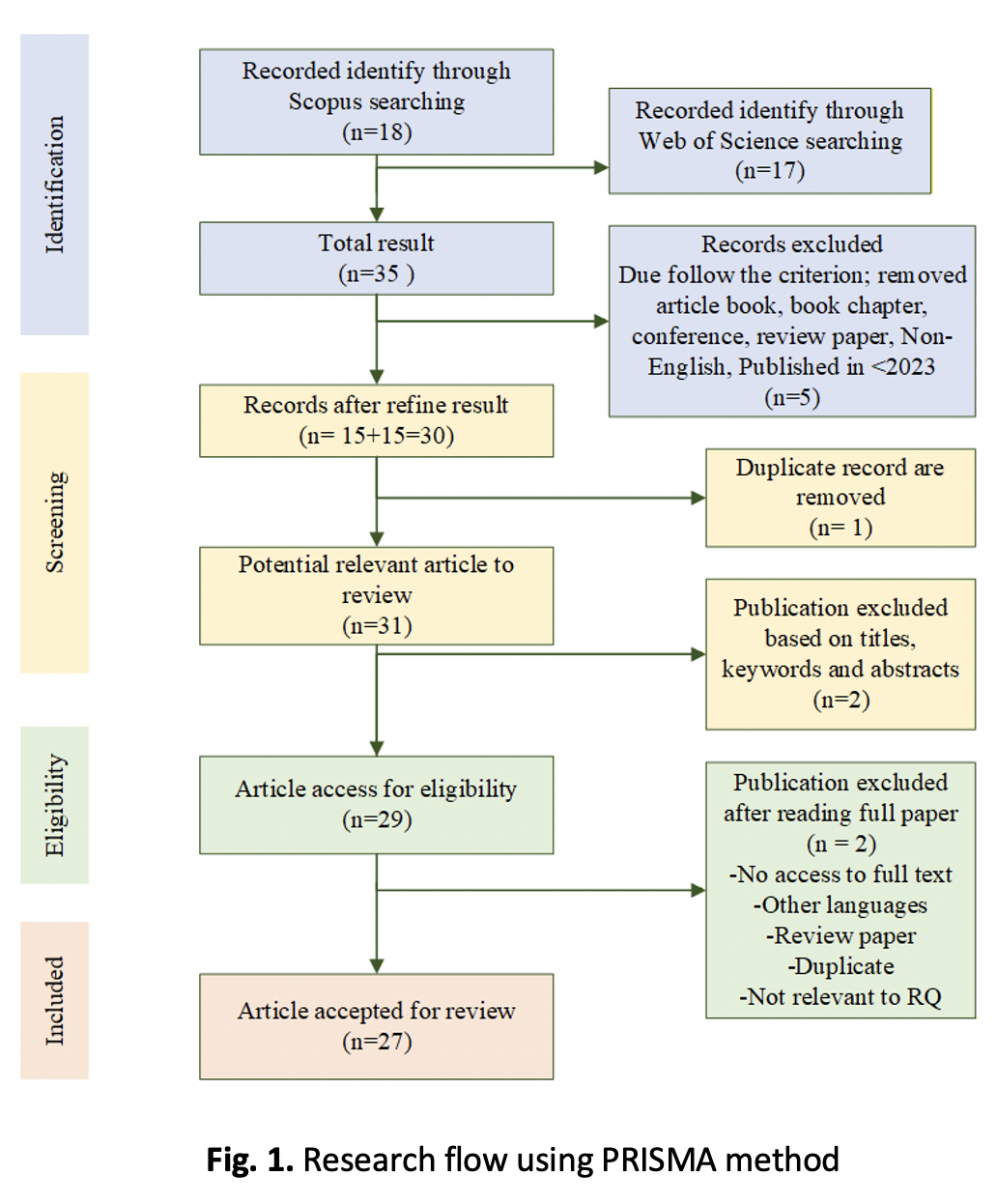
The rapid growth of renewable energy technologies, particularly photovoltaic generation coupled with battery energy storage, has introduced new challenges in maintaining efficiency, stability, and cost-effectiveness under variable operating conditions. Traditional monitoring and control strategies are often insufficient to manage the complex dynamics and multi-layer interactions of these hybrid systems. To address these challenges, the digital twin concept has emerged as a promising solution that bridges the physical and virtual environments. It enables real-time data synchronization, predictive analysis, and intelligent decision-making for improved energy management. However, its practical implementation in photovoltaic–battery systems remain fragmented, with many models focused on simulation rather than full cyber-physical integration. This gap highlights the need to identify current trends, strengths, and limitations in existing digital twin research. This study aims to systematically review recent developments in digital twin applications for photovoltaic and battery energy storage systems, outlining the key technological focus areas and research directions. The review follows the PRISMA methodology to ensure a structured and transparent selection of relevant literature. The analysis identifies four focus areas. The first, architecture and integration, emphasizes system modelling and real-time synchronization between sensors, IoT devices, and digital environments. The second, intelligent control and optimization, explores how artificial intelligence and predictive algorithms improve forecasting, scheduling, and operational efficiency. The third, reliability and predictive maintenance, focuses on diagnostics, degradation management, and fault prevention within hybrid energy systems. The fourth, sustainability and deployment, assesses techno-economic performance, carbon mitigation, and scalability for industrial and urban applications. Results show that integrating digital twin frameworks with artificial intelligence and optimization techniques enhances energy utilization, operational reliability, and cost efficiency. Nonetheless, further progress is required to standardize architecture, ensure secure data communication, and validate large-scale industrial deployment. In conclusion, digital twin integration provides a vital pathway toward intelligent, adaptive, and low-carbon energy infrastructures, enabling the transition from traditional management systems to real-time, data-driven operation in renewable energy networks.