Solar-Powered Adsorption Refrigeration and Desalination Systems for Sustainable Energy and Water Solutions: A Systematic Review of Key Factors, Challenges, and Performance Enhancements
Keywords:
ADS, ARS, PRISMA, sustainable water and energy solutionsAbstract
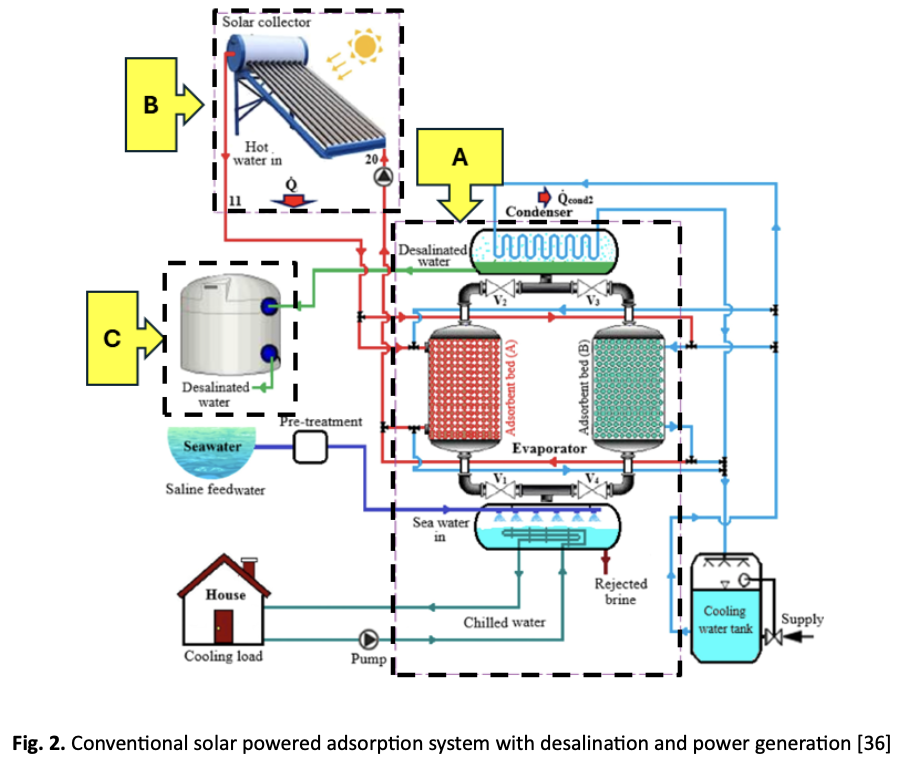
The increasing demand for air-conditioning and freshwater is contributing to climate change and heightening water scarcity, particularly in remote and island communities. Solar-powered adsorption refrigeration (ARS) and adsorption desalination (ADS) systems offer sustainable, low-carbon alternatives to conventional cooling and desalination technologies. This paper presents a systematic review of ARS and ADS systems, focusing on key performance factors, technical challenges, and recent advancements aimed at enhancing system efficiency. Using the PRISMA methodology, relevant studies are selected and analyzed to ensure a transparent and reproducible review process. Key performance-influencing factors are identified and analyzed from existing literature, with a focus on system performance. The review highlights critical design parameters, material selection, cycle configurations, and integration strategies that influence system performance. It also discusses the limitations and knowledge gaps that need to be addressed for real-world deployment. Furthermore, the study highlights optimization strategies employed across various designs to enhance system integration and reliability. The findings provide critical insights into implementing ARS-ADS systems in island settings, supporting climate adaptation and sustainable development goals in off-grid or resource-constrained areas.