The Effect of Glutaraldehyde Crosslinking on the Performance of Hybrid PVA-Chitosan-Polyaniline Hydrogel for Solar Vapor Generation
Keywords:
Polymer Hydrogel, Solar Vapor Generation, PolyanilineAbstract
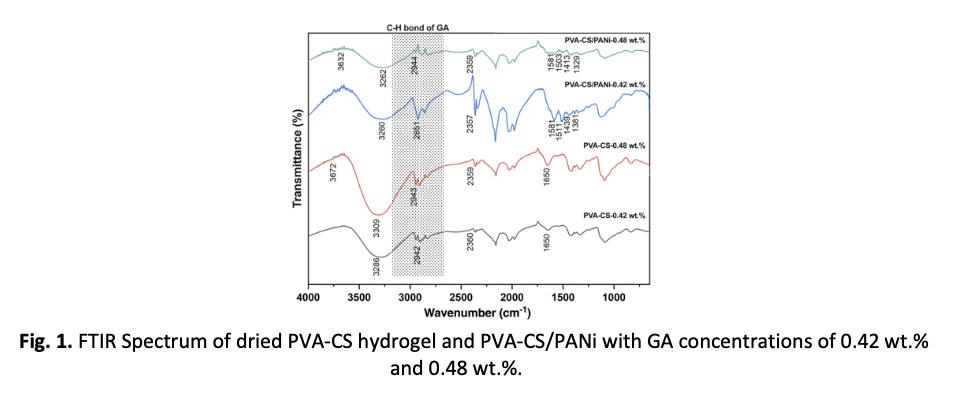
Solar Vapor Generation (SVG) stands out as a potent solution among other options, harnessing abundant solar energy to generate clean water through an evaporation process similar to the natural water cycle. Crosslinkers are fundamental components in the design and functionality of polymer hydrogel for SVG applications. The primary role of a crosslinker is to establish the three-dimensional network structure of hydrogels, which directly governs mechanical properties, water transport efficiency, and overall performance in solar-driven evaporation processes. The optimisation of crosslinkers leads to a more efficient SVG system. In this work, hybrid hydrogels of polyvinyl alcohol-chitosan (PVA-CS) and polyaniline (PANI) with varying concentrations of Glutaraldehyde (GA) were studied to evaluate the hydrogel’s rigidity and performance in facilitating the SVG system. Herein, we report the preparation of PVA-CS hydrogels with the addition of polyaniline (PANi) at different glutaraldehyde (GA) concentrations. PVA-CS hydrogels without PANi are denoted as PVA-CS-0.42 wt.% GA and PVA-CS-0.48 wt.% GA, whereas PVA-CS hydrogels with PANi are denoted as PVA-CS-0.42 wt.% GA- PANi and PVA-CS-0.48 wt.% GA-PANi. The PVA-CS hydrogel with PANi copolymers was prepared by solution polymerisation to incorporate PANi into the hydrogel network structure. The storage modulus of the PVA-CS hydrogels for all systems was determined by rheology. The storage modulus (G’) of PVA-CS-0.48 wt.% GA-PANi depicted the highest value of 2948 Pa compared to PVA-CS-0.42 wt.% GA-PANi, which depicted the G’ value of 2362 Pa. The Tan δ value of PVA-Chitosan-0.48 wt.% GA-PANi was 0.05, indicating elastic behaviour. From FTIR analysis, an absorption band was observed between 3600 and 3000 cm−1, attributed to the O-H and N-H groups of PVA and PANi, and was also evident in the PVA-CS hydrogel with the highest GA concentration, 0.48 wt.%. The microporous structure of PVA-Chitosan hydrogel with PANi distribution increases with higher concentration of GA, which demonstrates that the degree of cross-linking of PANi gives a more rigid structure of porous hydrogel. Therefore, it is expected that this hydrogel will scatter natural sunlight across its surface, efficiently converting light to heat at the evaporating surface, thereby supporting an efficient SVG design platform.