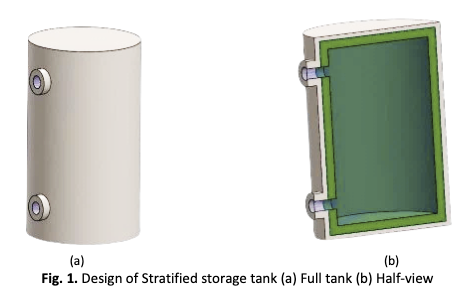
Enhanced Thermal Performance of Solar Heating Systems using Phase Change Materials in Stratified Water Storage Tanks
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/afhme.1.1.19aKeywords:
Solar system, thermal energy storage, PCM, computational fluid dynamicAbstract
Over the past few decades, there has been a steady increase in the use of solar water heaters in regions with abundant solar energy. However, because the sun can only provide electricity for a fraction of every 24-hour period, it is necessary to supplementsolar water heaters with thermal energy storage systems. These thermal water storage tanks for solar systems use phase change materials (PCMs), which can store additional energy to provide sufficient power, for example, to compensate for potential shortcomings that can arise from limited production time, such as at night or during cloudy weather. PCMs can undergo a solid-to-liquid phase transition (i.e. melting process) when heated to a temperature suitable for the heat input used. This study explores waysto improve the thermal efficiency of thermal water storage tanks by applying a potential digital model using PCM containing paraffin wax. This research aims to find the most suitable PCMs for finite element modelling, including detecting changes in thermal conductivity and enthalpy at different temperatures. Potential factors for increasing the efficiency include the use of encapsulated PCM for spheres on the heat exchanger and varying the time required for the melting/solidification process. The study also includes an overview of the Latent Heat Energy Storage System (LHESS) and its underlying theory.