Developing Aesthetic Immersive Experience (AIX) Model using Fuzzy Delphi Method for Virtual Reality Historical Event
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37934/picl.4.1.1839Keywords:
Virtual Reality, historical event, immersive experience, aesthetic, Fuzzy DelphiAbstract
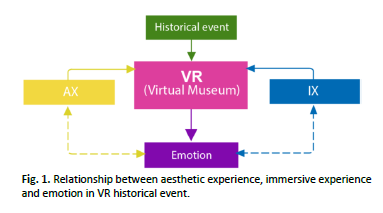
The user experience model is an indispensable tool for assessing the quality of immersive virtual reality (VR) technology. The design of the experience-based products involved creative approaches viewing from aesthetic perspectives. Thus, it indicates the need to develop a unifying aesthetic immersive experience (AIX) model with an expert's consent through the Fuzzy Delphi Method (FDM) to appraise the new experience. The model focuses on aesthetic experience and immersive experience constructs and elements; cognitive, perception, and emotional as scrutinised in the literature review. Hence, this paper aims to explain the development of the initial AIX model using FDM for VR historical events. The method implementation commenced with developing a survey of AIX elements using a seven-point linguistic scale, selecting experts, and determining linguistic variables based on the triangular fuzzy number, fuzzy scale level, defuzzification process, ranking, and formulation. The defuzzification value of each item consisting of the required threshold (d) value < 0.2 and percentage > 70% of expert consent to determine consensus on the survey items, as the alpha-cut (α-cut) value of ≥ 0.5 to select the AX and IX elements in the model. The d value for the accepted elements ranges between 0.109 and 0.191, and the α-cut value is shown between 0.627 and 0.873. After the defuzzification stage, the formulation instigates, which requires merging, combining, withdrawing, and renaming constructs and elements to denote the AIX model contextually. Thus, a consensus has been reached, with twelve constructs with respective twenty-five elements, which were then formulated into three constructs and sixteen elements to form the initial AIX model to develop virtual reality historical events. The findings create a new intervening input in creative fields and immersive experience design for virtual exploration in enhancing art and history education.
Downloads
References
[1] Liu, Rongrong, and Adzrool Idzwan Ismail. "AI Innovation in Architectural Design: Enhancing Aesthetic Experience with 'Midjourney'." Journal of Advanced Research Design 127, no. 1 (2025): 84–95. https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.127.1.8495
[2] Ekram, M., et al. "Revolutionizing Virtual Reality with Generative AI: An In-Depth Review." Journal of Advanced Research in Computing and Applications 30 (2023): 19–30.
[3] Ahmed, H., Abas, A. M., Binti, F., Aziz, A., and Hasan, R. "Review of Augmented Reality Applications in Manufacturing Engineering." Journal of Advanced Research in Computing and Applications 5 (2016): 11–16.
[4] Slater, M. "Immersion and the Illusion of Presence in Virtual Reality." John Wiley and Sons Ltd, August 1, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjop.12305
[5] Bowman, D. A., and McMahan, R. P. "Virtual Reality: How Much Immersion is Enough?" Computer 40, no. 7 (2007): 36–43. https://doi.org/10.1109/MC.2007.257
[6] Pillai, J. S., Schmidt, C., and Richir, S. "Achieving Presence Through Evoked Reality." Frontiers in Psychology 4, no. FEB (2013). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00086
[7] Jordan, P. W., Bardill, A., Herd, K., and Grimaldi, S. "Design for Subjective Wellbeing: Towards a Design Framework for Constructing Narrative." Design Journal 20, no. sup1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/14606925.2017.1352926
[8] Zou, N., Gong, Q., Zhou, J., Chen, P., Kong, W., and Chai, C. "Value-Based Model of User Interaction Design for Virtual Museum." Springer, June 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42486-021-00061-7
[9] Hagen, D., Creutzburg, R., and Hasche, E. "Virtual Reality, Augmented Reality, Mixed Reality & Visual Effects: New Potentials by Event Technology for the Immanuel Kant Anniversary 2024 in Kaliningrad." In Challenges by Cultural and Sport Mega Events: Socio-Economic and Environmental Effects, Proceedings of the International Conference, Kaliningrad: University Press Kaliningrad, December 2021, 52–62.
[10] Suroyo, B., Maulana Putra, B., Al-Fiqri, Y., Ibrahim, B., Noval Dwi Pratama, M., and AYani, J. "The Adoption of New Paradigm: Innovation of Virtual Reality (VR) Model Learning Based on Cultural Heritage of Bandar Senapelan to Assist Students in Education." Conference Proceedings 134 (2022): 43600.
[11] Melemez, K., Di Gironimo, G., Esposito, G., and Lanzotti, A. "Concept Design in Virtual Reality of a Forestry Trailer Using a QFD-TRIZ Based Approach." Turkish Journal of Agriculture and Forestry 37, no. 6 (2013): 789–801. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1302-29
[12] Leder, H., and Pelowski, M. "Empirical Aesthetics." In The Oxford Handbook of Empirical Aesthetics, Oxford University Press, 2021, 921–942. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780198824350.013.43
[13] Marković, S. "Components of Aesthetic Experience: Aesthetic Fascination, Aesthetic Appraisal, and Aesthetic Emotion." i-Perception 3, no. 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1068/i0450aap
[14] Schindler, I., et al. "Measuring Aesthetic Emotions: A Review of the Literature and a New Assessment Tool." Public Library of Science, June 1, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0178899
[15] Rani, N. A., Hashim, M. E. A., and Idris, M. Z. "Literature Survey: The Potential of Integrating Immersive Experience and Aesthetic Experience in Virtual Reality Historical Event." Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology 33, no. 3 (2024): 112–123. https://doi.org/10.37934/araset.33.3.112123
[16] McMahan, R. P., Gorton, D., Gresock, J., McConnell, W., and Bowman, D. A. "Separating the Effects of Level of Immersion and 3D Interaction Techniques." In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Virtual Reality Software and Technology (VRST), 2006. https://doi.org/10.1145/1180495.1180518
[17] Kim, Bokyung. "Virtual Reality as an Artistic Medium: A Study on Creative Projects Using Contemporary Head-Mounted Displays." 2016.
[18] Heeter, C. "Being There: The Subjective Experience of Presence." Presence: Teleoperators and Virtual Environments 1, no. 2 (1992): 262–271. https://doi.org/10.1162/pres.1992.1.2.262
[19] Rahaman, H. "Digital Heritage Interpretation: A Conceptual Framework." Digital Creativity 29, no. 2–3 (2018): 208–234. https://doi.org/10.1080/14626268.2018.1511602
[20] Suh, A., and Prophet, J. "The State of Immersive Technology Research: A Literature Analysis." Computers in Human Behavior 86 (2018): 77–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.04.019
[21] Huggett, J. "Virtually Real or Really Virtual: Towards a Heritage Metaverse?" Studies in Digital Heritage 4, no. 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.14434/sdh.v4i1.26218
[22] Vinayagamoorthy, V., Brogni, A., Gillies, M., Slater, M., and Steed, A. "An Investigation of Presence Response Across Variations in Visual Realism." The 7th Annual International Presence Workshop (2004): 148–155.
[23] Selzer, M. N., and Castro, S. M. "Immersion Metrics for Virtual Reality." June 2022.
[24] Leonardis, D., Frisoli, A., Barsotti, M., Carrozzino, M., and Bergamasco, M. "Multi-Sensory Feedback Can Enhance Embodiment Within an Enriched Virtual Walking Scenario." Presence 23, no. 3 (2014): 253–266.
[25] Pan, Y. "VR Reality of the Relationship Between Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality in the Context of Virtual Reality." In Journal of Physics: Conference Series, IOP Publishing Ltd, November 2021. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/2066/1/012056
[26] Aylett, R., and Louchart, S. "Towards a Narrative Theory of Virtual Reality." Virtual Reality 7, no. 1 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10055-003-0114-9
[27] Aylett, R. "Narrative in Virtual Environments – Towards Emergent Narrative." 1999.
[28] Leder, H., Belke, B., Oeberst, A., and Augustin, D. "A Model of Aesthetic Appreciation and Aesthetic Judgments." British Journal of Psychology 95, no. 4 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1348/0007126042369811
[29] Moens, B. G. "Aesthetic Experience in Virtual Museums: A Postphenomenological Perspective." 2018. https://doi.org/10.14434/sdh.v2i1.24468
[30] Vindenes, J., and Wasson, B. "A Postphenomenological Framework for Studying User Experience of Immersive Virtual Reality." Frontiers in Virtual Reality 2 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3389/frvir.2021.656423
[31] Kim, Bokyung. "Virtual Reality as an Artistic Medium: A Study on Creative Projects Using Contemporary Head-Mounted Displays." 2016.
[32] Marković, S. "Components of Aesthetic Experience: Aesthetic Fascination, Aesthetic Appraisal, and Aesthetic Emotion." i-Perception 3, no. 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1068/i0450aap
[33] Champion, E. History and Cultural Heritage in Virtual Environments. Oxford University Press, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199826162.013.020
[34] Dogan, E., and Kan, M. H. "Bringing Heritage Sites to Life for Visitors: Towards a Conceptual Framework for Immersive Experience." Advances in Hospitality and Tourism Research 8, no. 1 (2020). https://doi.org/10.30519/ahtr.630783
[35] Tcha-Tokey, K., Christmann, O., Loup-Escande, E., Loup, G., and Richir, S. "Towards a Model of User Experience in Immersive Virtual Environments." Advances in Human-Computer Interaction 2018 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/7827286
[36] Chrysanthakopoulou, A., Kalatzis, K., and Moustakas, K. "Immersive Virtual Reality Experience of Historical Events Using Haptics and Locomotion Simulation." Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 11, no. 24 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/app112411613
[37] Wu, H., Cai, T., Luo, D., Liu, Y., and Zhang, Z. "Immersive Virtual Reality News: A Study of User Experience and Media Effects." International Journal of Human Computer Studies 147 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhcs.2020.102576
[38] Zarour, M., and Alharbi, M. "User Experience Framework That Combines Aspects, Dimensions, and Measurement Methods." Cogent Engineering 4, no. 1 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2017.1421006
[39] Rubio-Tamayo, J. L., Barrio, M. G., and García, F. G. "Immersive Environments and Virtual Reality: Systematic Review and Advances in Communication, Interaction and Simulation." Multimodal Technologies and Interaction, December 1, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti1040021
[40] Saifulizam, Minhah Mardhiyyah, Ismahafezi Ismail, Wan Mohd Amir Fazamin Wan Hamzah, Maizan Mat Amin, and Hoshang Kolivand. "A Systematic Literature Review: User Experience in Virtual Reality Prototyping." Journal of Advanced Research Design 123, no. 1 (2024): 91-107. https://doi.org/10.37934/ard.123.1.91107
[41] Hashim, M. E. A. H. "Development of A Hexagon Aesthetic User Experience Model for Augmented Reality Comics." Universiti Pendidikan Sultan Idris, 2022.
[42] Hashim, M. E. A., Idris, M. Z., and Said, C. S. "The Heptagon of AUX Model: Development of a Synergising Model on Aesthetic Experience and User Experience Through the Fuzzy Delphi Method Towards Augmented Reality Comics." Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering 429 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-99188-3_19
[43] Ismail, K., Ishak, R., and Kamaruddin, S. H. "Development of Professional Learning Communities Model Using Fuzzy Delphi Approach." TEM Journal 10, no. 2 (2021): 872–878. https://doi.org/10.18421/TEM102-48
[44] Azargoon, M., Shabani, A., Cheshmehsohrabi, M., and Asemi, A. "Identification of Effective Factors on the Use of ‘Query Suggestions’ Through Fuzzy Delphi Method." 2019.
[45] Diodato, R. "Virtual Reality and Aesthetic Experience." Philosophies 7, no. 2 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/philosophies7020029
[46] Brinck, I. "Empathy, Engagement, Entrainment: The Interaction Dynamics of Aesthetic Experience." Cognitive Processing 19, no. 2 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-017-0805-x
[47] Moens, B. G. "Aesthetic Experience in Virtual Museums: A Postphenomenological Perspective." 2018. https://doi.org/10.14434/sdh.v2i1.24468
[48] Redies, C. "Combining Universal Beauty and Cultural Context in a Unifying Model of Visual Aesthetic Experience." Frontiers in Human Neuroscience 9, no. APR (2015): 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2015.00218
[49] Leder, H., and Nadal, M. "Ten Years of a Model of Aesthetic Appreciation and Aesthetic Judgments: The Aesthetic Episode – Developments and Challenges in Empirical Aesthetics." British Journal of Psychology 105, no. 4 (2014): 443–464. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjop.12084
[50] Hassan, N. M. H. N., et al. "Unveiling Collaborative Trends in Fuzzy Delphi Method (FDM) Research: A Co-Authorship Bibliometrics Study." International Journal of Advanced Research in Computational Thinking and Data Science 2 (2024): 1–20.
[51] Rani, N. B. A., Hashim, M. E. A. B., Mustafa, W. A., Idris, M. Z. B., Al-Jawahry, H. M., and Ramadan, G. M. "Applying Fuzzy Delphi Method (FDM) to Obtain the Expert Consensus in Aesthetic Experience (Ax) and Immersive Experience (Ix) Elements for Virtual Reality Historical Event (VR Historical Event)." In 3rd IEEE International Conference on Mobile Networks and Wireless Communications (ICMNWC), 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICMNWC60182.2023.10435812
[52] Roy, T. K., and Garai, A. "Intuitionistic Fuzzy Delphi Method: More Realistic and Interactive Forecasting Tool." Notes on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Sets 18, no. 2 (2012): 37–50.
[53] Clayton, M. J. "Delphi: A Technique to Harness Expert Opinion for Critical Decision-Making Tasks in Education." Educational Psychology 17, no. 4 (1997): 373–386. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144341970170401
[54] Mustapha, R., and Darusalam, G. Aplikasi Kaedah Fuzzy Delphi Dalam Penyelidikan Sains Sosial. Kuala Lumpur: UM Press, 2018.
[55] Benítez, J. M., Martín, J. C., and Román, C. "Using Fuzzy Number for Measuring Quality of Service in the Hotel Industry." Tourism Management 28, no. 2 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2006.04.018
[56] Chang, P. L., Hsu, C. W., and Chang, P. C. "Fuzzy Delphi Method for Evaluating Hydrogen Production Technologies." International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, October 2011: 14172–14179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.05.045
[57] Ganisen, S., Mohammad, I. S., Nesan, L. J., Mohammed, A. H., and Kanniyapan, G. "The Identification of Design for Maintainability Imperatives to Achieve Cost Effective Building Maintenance: A Delphi Study." Jurnal Teknologi 77, no. 30 (2015): 75–88. https://doi.org/10.11113/jt.v77.6871
[58] Mourhir, A., Rachidi, T., and Karim, M. "River Water Quality Index for Morocco Using a Fuzzy Inference System." Environmental Systems Research 3, no. 1 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40068-014-0021-y
[59] Saido, G. A. M., Siraj, S., DeWitt, D., and Al-Amedy, O. S. "Development of an Instructional Model for Higher Order Thinking in Science Among Secondary School Students: A Fuzzy Delphi Approach." International Journal of Science Education 40, no. 8 (2018): 847–866. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2018.1452307
[60] Pelowski, M., and Akiba, F. "A Model of Art Perception, Evaluation and Emotion in Transformative Aesthetic Experience." New Ideas in Psychology 29, no. 2 (2011): 80–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.newideapsych.2010.04.001
[61] Louchart, S., and Aylett, R. "Towards a Narrative Theory of Virtual Reality." Virtual Reality 7, no. 1 (2003).